Security News

SonicWall warned customers today to urgently patch multiple critical vulnerabilities impacting the company's Global Management System firewall management and Analytics network reporting engine software suites."This suite of vulnerabililtes, which was responsibility disclosed, includes four vulnerabilities with a CVSSv3 rating of CRITICAL, that allows an attacker to bypass authentication and could potentially result in exposure of sensitive information to an unauthorized actor," SonicWall said.

An authentication bypass vulnerability in the Arcserve Unified Data Protection enterprise data protection solution can be exploited to compromise admin accounts and take over vulnerable instances, MDSec researchers Juan Manuel Fernández and Sean Doherty have found - and have released a PoC exploit for it."At this time, Arcserve is not aware of any active attempts to exploit this vulnerability," the company said on Tuesday, when it pushed out fixes for the flaw.

Data protection vendor Arcserve has addressed a high-severity security flaw in its Unified Data Protection backup software that can let attackers bypass authentication and gain admin privileges.According to the company, Arcserve UDP is a data and ransomware protection solution designed to help customers thwart ransomware attacks, restore compromised data, and enable effective disaster recovery to ensure business continuity.

Grafana has released security fixes for multiple versions of its application, addressing a vulnerability that enables attackers to bypass authentication and take over any Grafana account that uses Azure Active Directory for authentication. Grafana is a widely used open-source analytics and interactive visualization app that offers extensive integration options with a wide range of monitoring platforms and applications.

Tired of those annoying CAPTCHA images that leave you feeling like you're solving a puzzle just to log in online? Learn how to use Apple's "CAPTCHA killer" feature called Automatic Verification in iOS 16. CAPTCHAs can be quite annoying when you just want to try to create a new account or log in to a website.

VMware has addressed multiple high-severity security flaws in vCenter Server, which can let attackers gain code execution and bypass authentication on unpatched systems. vCenter Server is the control center for VMware's vSphere suite and a server management solution that helps admins manage and monitor virtualized infrastructure.

A report from the Microsoft Defender Experts reveals a new multi-staged adversary in the middle phishing attack combined with a business email compromise attack targeting banking and financial institutions. The phishing email impersonates one of the target's trusted vendors to appear more legitimate and blend with legitimate email traffic and bypass detections, especially when an organization has policies to automatically allow emails from trusted vendors.

The Vivaldi Browser is now spoofing Microsoft Edge on Android devices starting today to bypass browser restrictions Microsoft placed in Bing Chat. Since Microsoft released its Bing Chat, they have restricted it so users can only use it on the Microsoft Edge Browser.

Researchers have discovered a novel attack on the Python Package Index repository that employs compiled Python code to sidestep detection by application security tools. PYC files are compiled bytecode files that are generated by the Python interpreter when a Python program is executed.
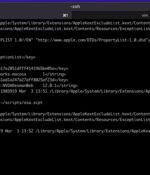
Microsoft has shared details of a now-patched flaw in Apple macOS that could be abused by threat actors with root access to bypass security enforcements and perform arbitrary actions on affected devices. "The most straight-forward implication of a SIP bypass is that an attacker can create files that are protected by SIP and therefore undeletable by ordinary means," Microsoft researchers Jonathan Bar Or, Michael Pearse, and Anurag Bohra said.