Security News > 2022 > August

Microsoft says the Outlook email client will crash when opening and reading emails with tables such as Uber receipt emails. "When opening, replying, or forwarding some emails that include complex tables, Outlook stops responding," the company explains in a support document.

New research from Kaspersky exposes a rootkit dubbed CosmicStrand, which sits quietly in the Unified Extensible Firmware Interface of specific computers. According to Kaspersky, the rootkit is located in the firmware images of Gigabyte or ASUS motherboards.

The ALPHV ransomware gang, aka BlackCat, claimed responsibility for a cyberattack against Creos Luxembourg S.A. last week, a natural gas pipeline and electricity network operator in the central European country. Creos' owner, Encevo, who operates as an energy supplier in five EU countries, announced on July 25 that they had suffered a cyberattack the previous weekend, between July 22 and 23.

Different cloud providers and private cloud platforms may offer similar capabilities but different ways of implementing security controls, along with disparate management tools. Old Security Tools No Longer Effective in the Cloud Security tools not born in the cloud are ill-equipped to protect applications running in the cloud for many reasons.

Amazon has revealed that it gives police videos from its Ring doorbells without a warrant and without user consent. The Amazon company responded to an inquiry from US Senator Ed Markey, confirming that there have been 11 cases in 2022 where Ring complied with police "Emergency" requests.

Cyber executives may not be sufficiently prioritizing threats from vulnerabilities within the value chain, beyond the immediate boundaries of their own organizations, according to Tata Consultancy Services. This Help Net Security video highlights how confident executives are about their cyber strategy.

Akamai Technologies squelched the largest-ever distributed denial-of-service attack in Europe earlier this month against a company that was being consistently hammered over a 30-day period. The user datagram protocol was the most popular vector used in the attack and was seen in the record spikes.

Ransomware attacks are in decline, according to reports by several cybersecurity companies. Two US states recently prohibited state agencies, counties and minicipalities from paying a ransom in response to a ransomware incident.

How can a CISO effectively explain the cost of a data breach to the company's Board? What type of information drives the point home for a non-technical audience? To explain the cost of a breach is highly dependent on the breach itself.
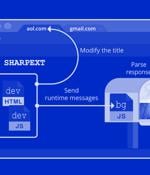
A threat actor operating with interests aligned with North Korea has been deploying a malicious extension on Chromium-based web browsers that's capable of stealing email content from Gmail and AOL. Cybersecurity firm Volexity attributed the malware to an activity cluster it calls SharpTongue, which is said to share overlaps with an adversarial collective publicly referred to under the name Kimsuky. SharpTongue has a history of singling out individuals working for organizations in the U.S., Europe, and South Korea who "Work on topics involving North Korea, nuclear issues, weapons systems, and other matters of strategic interest to North Korea," researchers Paul Rascagneres and Thomas Lancaster said.