Security News
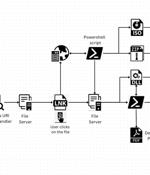
A legitimate Windows search feature is being exploited by malicious actors to download arbitrary payloads from remote servers and compromise targeted systems with remote access trojans such as AsyncRAT and Remcos RAT. The novel attack technique, per Trellix, takes advantage of the "Search-ms:" URI protocol handler, which offers the ability for applications and HTML links to launch custom local searches on a device, and the "Search:" application protocol, a mechanism for calling the desktop search application on Windows. It's worth noting that clicking on the link also generates a warning "Open Windows Explorer?," approving which "The search results of remotely hosted malicious shortcut files are displayed in Windows Explorer disguised as PDFs or other trusted icons, just like local search results," the researchers explained.
Businesses operating in the Latin American region are the target of a new Windows-based banking trojan called TOITOIN since May 2023. "This sophisticated campaign employs a trojan that follows a multi-staged infection chain, utilizing specially crafted modules throughout each stage," Zscaler researchers Niraj Shivtarkar and Preet Kamal said in a report published last week.
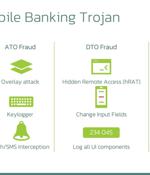
A new Android malware campaign has been observed pushing the Anatsa banking trojan to target banking customers in the U.S., U.K., Germany, Austria, and Switzerland since the start of March 2023. "The actors behind Anatsa aim to steal credentials used to authorize customers in mobile banking applications and perform Device-Takeover Fraud to initiate fraudulent transactions," ThreatFabric said in an analysis published Monday.

ThreatFabric discovered a previous Anatsa campaign on Google Play in November 2021, when the trojan was installed over 300,000 times by impersonating PDF scanners, QR code scanners, Adobe Illustrator apps, and fitness tracker apps. In March 2023, after a six-month hiatus in malware distribution, the threat actors launched a new malvertizing campaign that leads prospective victims to download Anatsa dropper apps from Google Play.
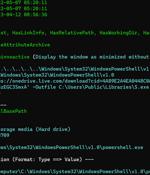
A new phishing campaign codenamed MULTI#STORM has set its sights on India and the U.S. by leveraging JavaScript files to deliver remote access trojans on compromised systems. The multi-stage attack chain commences when an email recipient clicks the embedded link pointing to a password-protected ZIP file hosted on Microsoft OneDrive with the password "12345."
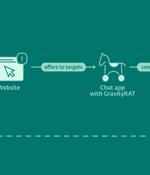
An updated version of an Android remote access trojan dubbed GravityRAT has been found masquerading as messaging apps BingeChat and Chatico as part of a narrowly targeted campaign since June 2022. "Notable in the newly discovered campaign, GravityRAT can exfiltrate WhatsApp backups and receive commands to delete files," ESET researcher Lukáš Štefanko said in a new report published today.

Qakbot - banking malware-turned-malware/ransomware distribution network - has been first observed in 2007 and is active to this day. "Qakbot operators tend to reduce or stop their spamming attacks for long periods of time on a seasonal basis, returning to activity with a modified suite of tools," Chris Formosa and Steve Rudd, researchers with Lumen's Black Lotus Labs, have noted.
A new open source remote access trojan called DogeRAT targets Android users primarily located in India as part of a sophisticated malware campaign. The malware is distributed via social media and messaging platforms under the guise of legitimate applications like Opera Mini, OpenAI ChatGOT, and Premium versions of YouTube, Netflix, and Instagram.
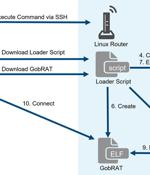
Linux routers in Japan are the target of a new Golang remote access trojan called GobRAT. "Initially, the attacker targets a router whose WEBUI is open to the public, executes scripts possibly by using vulnerabilities, and finally infects the GobRAT," the JPCERT Coordination Center said in a report published today. The compromise of an internet-exposed router is followed by the deployment of a loader script that acts as a conduit for delivering GobRAT, which, when launched, masquerades as the Apache daemon process to evade detection.
In yet another instance of how threat actors are abusing Google Ads to serve malware, a threat actor has been observed leveraging the technique to deliver a new Windows-based financial trojan and information stealer called LOBSHOT. "LOBSHOT continues to collect victims while staying under the radar," Elastic Security Labs researcher Daniel Stepanic said in an analysis published last week. The American-Dutch company attributed the malware strain to a threat actor known as TA505 based on infrastructure historically connected to the group.