Security News

The U.S. Cybersecurity and Infrastructure Security Agency (CISA) has added a critical security flaw impacting Jenkins to its Known Exploited Vulnerabilities (KEV) catalog, following its...

CISA has added a critical Jenkins vulnerability that can be exploited to gain remote code execution to its catalog of security bugs, warning that it's actively exploited in attacks. [...]
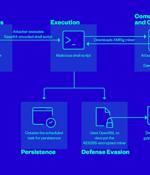
Cybersecurity researchers have found that it's possible for attackers to weaponize improperly configured Jenkins Script Console instances to further criminal activities such as cryptocurrency mining. Jenkins, a popular continuous integration and continuous delivery platform, features a Groovy script console that allows users to run arbitrary Groovy scripts within the Jenkins controller runtime.

Prioritizing cybercrime intelligence for effective decision-making in cybersecurityIn this Help Net Security interview, Alon Gal, CTO at Hudson Rock, discusses integrating cybercrime intelligence into existing security infrastructures. Proactive cybersecurity: A strategic approach to cost efficiency and crisis managementIn this Help Net Security interview, Stephanie Hagopian, VP of Security at CDW, discusses offensive strategies in the face of complex cyberattacks and the role of the zero-trust model.

The number of public-facing installs of Jenkins servers vulnerable to a recently disclosed critical vulnerability is in the tens of thousands. Trailing them are India, Germany, Republic of Korea, France, and the UK. The revelation of the vast attack surface comes days after multiple exploits were made public on January 26 - themselves released just two days after the coordinated disclosure from Jenkins and Yaniv Nizry, the researcher at Sonar who first discovered the vulnerability.

Researchers found roughly 45,000 Jenkins instances exposed online that are vulnerable to CVE-2023-23897, a critical remote code execution flaw for which multiple public proof-of-concept exploits are in circulation. Depending on the instance's configuration, attackers could decrypt stored secrets, delete items from Jenkins servers, and download Java heap dumps.

Several proof-of-concept exploits for a recently patched critical vulnerability in Jenkins have been made public and there's evidence of exploitation in the wild. Jenkins is a widely used Java-based open-source automation server that helps developers build, test and deploy applications, enabling continuous integration and continuous delivery.

Multiple proof-of-concept exploits for a critical Jenkins vulnerability allowing unauthenticated attackers to read arbitrary files have been made publicly available, with some researchers reporting attackers actively exploiting the flaws in attacks. SonarSource researchers discovered two flaws in Jenkins that could enable attacks to access data in vulnerable servers and execute arbitrary CLI commands under certain conditions.

The maintainers of the open-source continuous integration/continuous delivery and deployment (CI/CD) automation software Jenkins have resolved nine security flaws, including a critical bug that,...
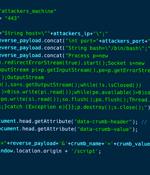
A pair of severe security vulnerabilities have been disclosed in the Jenkins open source automation server that could lead to code execution on targeted systems. The flaws, tracked as CVE-2023-27898 and CVE-2023-27905, impact the Jenkins server and Update Center, and have been collectively christened CorePlague by cloud security firm Aqua.