Security News

Threat actors are increasingly abusing Internet Information Services extensions to backdoor servers as a means of establishing a "Durable persistence mechanism." Attack chains taking this approach commence with weaponizing a critical vulnerability in the hosted application for initial access, using this foothold to drop a script web shell as the first stage payload. This web shell then becomes the conduit for installing a rogue IIS module to provide highly covert and persistent access to the server, in addition to monitoring incoming and outgoing requests as well as running remote commands.

Microsoft says attackers increasingly use malicious Internet Information Services web server extensions to backdoor unpatched Exchange servers as they have lower detection rates compared to web shells. Microsoft previously saw custom IIS backdoors installed after threat actors exploited ZOHO ManageEngine ADSelfService Plus and SolarWinds Orion vulnerabilities.

Microsoft says attackers increasingly use malicious Internet Information Services web server extensions to backdoor unpatched Exchange servers as they have lower detection rates compared to web shells. "In most cases, the actual backdoor logic is minimal and cannot be considered malicious without a broader understanding of how legitimate IIS extensions work, which also makes it difficult to determine the source of infection," the Microsoft 365 Defender Research Team said Tuesday.

A newly discovered malware has been put to use in the wild at least since March 2021 to backdoor Microsoft Exchange servers belonging to a wide range of entities worldwide, with infections lingering in 20 organizations as of June 2022. Dubbed SessionManager, the malicious tool masquerades as a module for Internet Information Services, a web server software for Windows systems, after exploiting one of the ProxyLogon flaws within Exchange servers.

Malicious actors are deploying a previously undiscovered binary, an Internet Information Services webserver module dubbed "Owowa," on Microsoft Exchange Outlook Web Access servers with the goal of stealing credentials and enabling remote command execution. "Owowa is a C#-developed.NET v4.0 assembly that is intended to be loaded as a module within an IIS web server that also exposes Exchange's Outlook Web Access," Kaspersky researchers Paul Rascagneres and Pierre Delcher said.

Threat actors are installing a malicious IIS web server module named 'Owowa' on Microsoft Exchange Outlook Web Access servers to steal credentials and execute commands on the server remotely.Microsoft Exchange servers are commonly targeted with web shells that allow threat actors to remotely execute commands on a server and are usually the focus of defenders.
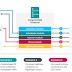
A systematic analysis of attacks against Microsoft's Internet Information Services servers has revealed as many as 14 malware families, 10 of them newly documented, indicating that the Windows-based web server software continues to be a hotbed for natively developed malware for close to eight years. IIS is an extensible web server software developed by Microsoft, enabling developers to take advantage of its modular architecture and use additional IIS modules to expand on its core functionality.

A new highly capable and persistent threat actor has been targeting major high-profile public and private entities in the U.S. as part of a series of targeted cyber intrusion attacks by exploiting internet-facing Microsoft Internet Information Services servers to infiltrate their networks. "TG1021 uses a custom-made malware framework, built around a common core, tailor-made for IIS servers. The toolset is completely volatile, reflectively loaded into an affected machine's memory and leaves little-to-no trace on infected targets," the researchers said.

A trio of researchers at Palo Alto Networks has detailed vulnerabilities in the JET database engine, and demonstrated how those flaws can be exploited to ultimately execute malicious code on systems running Microsoft's SQL Server and Internet Information Services web server.In a talk today at Black Hat Asia titled Give Me a SQL Injection, I Shall PWN IIS and SQL Server, the three explained they found the JET engine - for years an underlying tech for Microsoft Access and other products, and still downloadable today - has many vulnerabilities.

It's patching time again for Windows Server 2016 and Windows 10 Oops! Microsoft has published an advisory on a bug in its Internet Information Services (IIS) product that allows a malicious HTTP/2...