Security News

Evilginx is an open-source man-in-the-middle attack framework designed to phish login credentials and session cookies, enabling attackers to bypass 2FA safeguards. “Back in 2017, I was...

Cybersecurity researchers have discovered a new PHP-based backdoor called Glutton that has been put to use in cyber attacks targeting China, the United States, Cambodia, Pakistan, and South...
A newly devised technique leverages a Windows accessibility framework called UI Automation (UIA) to perform a wide range of malicious activities without tipping off endpoint detection and response...
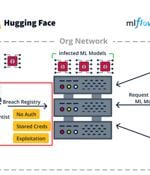
Cybersecurity researchers have disclosed multiple security flaws impacting open-source machine learning (ML) tools and frameworks such as MLflow, H2O, PyTorch, and MLeap that could pave the way...

Updated NIST guidelines reject outdated password security practices in favor of more effective protections. Learn from Specops Software about 6 takeaways from NIST's new guidance that help create...

Cybersecurity researchers have disclosed six security flaws in the Ollama artificial intelligence (AI) framework that could be exploited by a malicious actor to perform various actions, including...

In this Help Net Security interview, John Cohen, Executive Director, Program for Countering Hybrid Threats at the Center for Internet Security, discusses the four pillars of the National Framework...
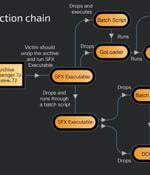
Russian-speaking users have become the target of a new phishing campaign that leverages an open-source phishing toolkit called Gophish to deliver DarkCrystal RAT (aka DCRat) and a previously...

Governance, risk, and compliance (GRC) frameworks help professionals assess an organization’s risk posture, align technological initiatives with business goals, and ensure regulatory compliance....

In this Help Net Security interview, Tom McAndrew, CEO at Coalfire, discusses the balance organizations must strike between legal compliance and effective enterprise security governance in the...