Security News

Users of Mirth Connect, an open-source data integration platform from NextGen HealthCare, are being urged to update to the latest version following the discovery of an unauthenticated remote code...
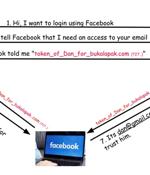
Critical security flaws have been disclosed in the Open Authorization (OAuth) implementation of popular online services such as Grammarly, Vidio, and Bukalapak, building upon previous shortcomings...

VMware has fixed a critical out-of-bounds write vulnerability and a moderate-severity information disclosure flaw in vCenter Server, its popular server management software.CVE-2023-34048 allows an attacker with network access to a vulnerable vCenter Server virtual appliance to trigger an out-of-bounds write that can lead to remote code execution.

VMware has released security updates to address a critical flaw in the vCenter Server that could result in remote code execution on affected systems. The issue, tracked as CVE-2023-34048 (CVSS...

VMware issued security updates to fix a critical vCenter Server vulnerability that can be exploited to gain remote code execution attacks on vulnerable servers. vCenter Server is the central management hub for VMware's vSphere suite, and it helps administrators manage and monitor virtualized infrastructure.

Takes rare step of issuing patches for end-of-life versions, as some staff report end-of-career letters VMware has disclosed a critical vulnerability in its vCenter Server – and that it issued an...

Citrix has urged admins to "Immediately" apply a fix for CVE-2023-4966, a critical information disclosure bug that affects NetScaler ADC and NetScaler Gateway, admitting it has been exploited. Plus, there's a proof-of-concept exploit, dubbed Citrix Bleed, now on GitHub.

After a six-day wait, Cisco started rolling out a patch for a critical bug that miscreants had exploited to install implants in thousands of devices. The flaw in the networking giant's IOS XE software, which allowed criminals to hijack thousands of Cisco switches and routers, first came to light last Monday.

Security researchers found three critical remote code execution vulnerabilities in the SolarWinds Access Rights Manager product that remote attackers could use to run code with SYSTEM privileges. SolarWinds ARM is a tool that enables organizations to manage and audit user access rights across their IT environments.

Microsoft says that the North Korean Lazarus and Andariel hacking groups are exploiting the CVE-2023-42793 flaw in TeamCity servers to deploy backdoor malware, likely to conduct software supply chain attacks. In September, TeamCity fixed a critical 9.8/10 vulnerability tracked as CVE-2023-42793 that allowed unauthenticated attackers to remotely execute code.