Security News > 2023 > July

All-In-One Security, a WordPress plugin installed on over one million sites, has issued a security update after a bug introduced in version 5.1.9 of the software caused users' passwords being added to the database in plaintext format. "This would be a problem if those site administrators were to try out those passwords on other services where your users might have used the same password. If those other services' logins are not protected by two-factor authentication, this could be a risk to the affected website."
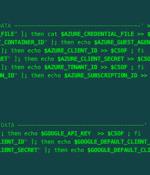
A malicious actor has been linked to a cloud credential stealing campaign in June 2023 that's focused on Azure and Google Cloud Platform services, marking the adversary's expansion in targeting beyond Amazon Web Services. They also overlap with an ongoing TeamTNT campaign disclosed by Aqua called Silentbob that leverages misconfigured cloud services to drop malware as part of what's said to be a testing effort, while also linking SCARLETEEL attacks to the threat actor, citing infrastructure commonalities.

Over the last few months, Clop ransomware gang has been exploiting a vulnerability in the MOVEit File Transfer utility to breach hundreds of companies to steal their data and attempt extortion against them. This week, Clop ransomware gang published Shutterfly's name on its data leak site, among other companies it has targeted, largely via the MOVEit SQL Injection vulnerability, tracked as CVE-2023-34362.
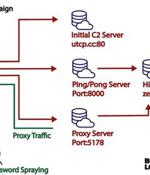
A new malware strain has been found covertly targeting small office/home office routers for more than two years, infiltrating over 70,000 devices and creating a botnet with 40,000 nodes spanning 20 countries. Lumen Black Lotus Labs has dubbed the malware AVrecon, making it the third such strain to focus on SOHO routers after ZuoRAT and HiatusRAT over the past year.

Zimbra has warned of a critical zero-day security flaw in its email software that has come under active exploitation in the wild. Additional details about the flaw are currently unavailable.

Since at least May 2021, stealthy Linux malware called AVrecon was used to infect over 70,000 Linux-based small office/home office routers to a botnet designed to steal bandwidth and provide a hidden residential proxy service. According to Lumen's Black Lotus Labs threat research team, while the AVrecon remote access trojan compromised over 70,000 devices, only 40,000 were added to the botnet after gaining persistence.

Since at least May 2021, stealthy Linux malware called AVrecon was used to infect over 70,000 Linux-based small office/home office routers to a botnet designed to steal bandwidth and provide a hidden residential proxy service. According to Lumen's Black Lotus Labs threat research team, while the AVrecon remote access trojan compromised over 70,000 devices, only 40,00 were added to the botnet after gaining persistence.

72% of hackers are confident that AI cannot replace human creativity in security research and vulnerability management, according to Bugcrowd. Generative AI was a major theme in the 2023 report, with 55% of respondents saying that it can already outperform hackers or will be able to do so within the next five years.

Researchers from Ruhr University Bochum and the CISPA Helmholtz Center for Information Security in Saarbrücken have assessed the security mechanisms of satellites currently orbiting the Earth from an IT perspective. They analyzed three current low-earth orbit satellites and found that, from a technical point of view, only some modern security concepts were implemented.

While trends in phishing frequently evolve, Facebook and Microsoft's collective dominance as the most spoofed brands continues, according to Vade. Facebook and Microsoft's collective dominance as the most spoofed brands continued into H1 2023, with the former accounting for 18% of all phishing URLs and the latter accounting for 15%. Microsoft experienced increase in spoofing attempts.