Security News

A new Go-based malware threat that researchers call Redigo has been targeting Redis servers vulnerable to CVE-2022-0543 to plant a stealthy backdoor and allow command execution. Today, AquaSec reports that its Redis honeypots vulnerable to CVE-2022-0543 caught a new piece of malware that is not detected as a threat by antivirus engines on Virus Total.

A new Go-based malware threat that researchers call Redigo has been targeting Redis servers vulnerable to CVE-2022-0543 to plant a stealthy backdoor and allow command execution. Today, AquaSec reports that its Redis honeypots vulnerable to CVE-2022-0543 caught a new piece of malware that is not detected as a threat by antivirus engines on Virus Total.

Updates to Windows Server released as part of this month's Patch Tuesday onslaught might cause some domain controllers to stop working or automatically restart, according to Microsoft. The enterprise software behemoth said organizations installing KB5019966 or later updates on domain controllers could see a memory leak with the Local Security Authority Subsystem Service.

"LSASS might use more memory over time and the DC might become unresponsive and restart," Microsoft explains on the Windows Health dashboard. "Depending on the workload of your DCs and the amount of time since the last restart of the server, LSASS might continually increase memory usage with the up time of your server and the server might become unresponsive or automatically restart."

Those affected may be unaware that their devices run services using the discontinued Boa web server, and that firmware updates and downstream patches do not address its known vulnerabilities. Boa is an open-source web server designed for embedded applications and used to access settings, management consoles, and sign-in screens in devices.
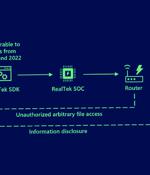
Microsoft said its own investigation into the attack activity uncovered Boa as a common link, assessing that the intrusions were directed against exposed IoT devices running the web server. "Despite being discontinued in 2005, the Boa web server continues to be implemented by different vendors across a variety of IoT devices and popular software development kits," the company said.

Microsoft said today that security vulnerabilities found to impact a web server discontinued since 2005 have been used to target and compromise organizations in the energy sector. The attackers gained access to the internal networks of the hacked entities via Internet-exposed cameras on their networks as command-and-control servers.

Were] two zero-days that [could] be chained together, with the first bug used remotely to open enough of a hole to trigger the second bug, which potentially allows remote code execution on the Exchange server itself. It does mean that an automated Python script can't just scan the whole internet and potentially exploit every Exchange server in the world in a matter of minutes or hours, as we saw happen with ProxyLogon and ProxyShell in 2021.

Microsoft is rolling out fixes for problems with the Kerberos network authentication protocol on Windows Server after it was broken by November Patch Tuesday updates. As we reported last week, updates released November 8 or later that were installed on Windows Server with the Domain Controller duties of managing network and identity security requests disrupted Kerberos authentication capabilities, ranging from failures in domain user sign-ins and Group Managed Service Accounts authentication to remote desktop connections not connecting.

Atlassian has released updates to address critical-severity updates in its centralized identity management platform, Crowd Server and Data Center, and in Bitbucket Server and Data Center, the company's solution for Git repository management. Rated critical, the issue in Crowd Server and Data Center is tracked as CVE-2022-43782 and is a misconfiguration that allows an attacker to bypass password checks when authenticating as the Crowd app and to call privileged API endpoints.