Security News

Threat actors have been abusing a bug in how Windows handles LNK files with non-standard target paths and internal structures to prevent in-built protections from stopping malicious payloads and trick users into running them. If the file is not listed, SmartScreen will prevent the file from being executed and show a warning.
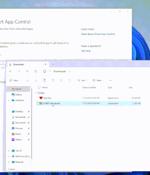
Cybersecurity researchers have uncovered design weaknesses in Microsoft's Windows Smart App Control and SmartScreen that could enable threat actors to gain initial access to target environments without raising any warnings. Smart App Control is a cloud-powered security feature introduced by Microsoft in Windows 11 to block malicious, untrusted, and potentially unwanted apps from being run on the system.
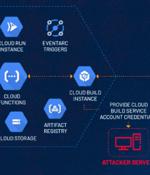
Cybersecurity researchers have disclosed a privilege escalation vulnerability impacting Google Cloud Platform's Cloud Functions service that an attacker could exploit to access other services and sensitive data in an unauthorized manner. "An attacker could escalate their privileges to the Default Cloud Build Service Account and access numerous services such as Cloud Build, storage, artifact registry and container registry," the exposure management company said in a statement.

GitHub is an immensely popular platform, with over 100 million developers and over 90% of Fortune 100 companies utilizing it. Despite its widespread use, many GitHub Actions workflows remain insecure, often due to excessive privileges or high-risk dependencies.

Multiple security flaws have been disclosed in Emerson Rosemount gas chromatographs that could be exploited by malicious actors to obtain sensitive information, induce a denial-of-service (DoS)...
Cybersecurity researchers have disclosed details of a now-patched security flaw in Phoenix SecureCore UEFI firmware that affects multiple families of Intel Core desktop and mobile processors....

The Kraken crypto exchange disclosed today that alleged security researchers exploited a zero-day website bug to steal $3 million in cryptocurrency and then refused to return the funds. The hack was disclosed by Kraken Chief Security Officer Nick Percoco on X, explaining that the exchange's security team received a vague bug report on June 9th about an "Extremely critical" that allowed anyone to increase the balances in a Kraken wallet artificially.

Cybersecurity researchers have uncovered a new suspicious package uploaded to the npm package registry that's designed to drop a remote access trojan (RAT) on compromised systems. The package in...

Now-patched authorization bypass issues impacting Cox modems that could have been abused as a starting point to gain unauthorized access to the devices and run malicious commands. "This series of...

Your profile can be used to present content that appears more relevant based on your possible interests, such as by adapting the order in which content is shown to you, so that it is even easier for you to find content that matches your interests. Content presented to you on this service can be based on your content personalisation profiles, which can reflect your activity on this or other services, possible interests and personal aspects.