Security News

Cybersecurity researchers have disclosed details of two medium-security flaws in Mitel 6800/6900 desk phones that, if successfully exploited, could allow an attacker to gain root privileges on the devices. Tracked as CVE-2022-29854 and CVE-2022-29855, the access control issues were discovered by German penetration testing firm SySS, following which patches were shipped in May 2022.

Researchers warn Bluetooth signals can be used to track device owners via a unique fingerprinting of the radio signal. The paper suggests that minor manufacturing imperfections in hardware are unique with each device, and cause measurable distortions which can be used as a "Fingerprint to track a specific device".

Security researchers at Intezer and BlackBerry have documented Symbiote, a wholly unique, multi-purpose piece of Linux malware that is nearly impossible to detect. "What makes Symbiote different from other Linux malware that we usually come across, is that it needs to infect other running processes to inflict damage on infected machines. Instead of being a standalone executable file that is run to infect a machine, it is a shared object library that is loaded into all running processes using LD PRELOAD, and parasitically infects the machine," the researchers pointed out.
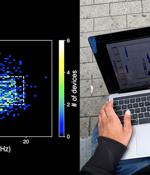
A new research undertaken by a group of academics from the University of California San Diego has revealed for the first time that Bluetooth signals can be fingerprinted to track smartphones. "To perform a physical-layer fingerprinting attack, the attacker must be equipped with a Software Defined Radio sniffer: a radio receiver capable of recording raw IQ radio signals," the researchers said in a new paper titled "Evaluating Physical-Layer BLE Location Tracking Attacks on Mobile Devices."

"The rise and proliferation of cryptocurrency has also provided attackers with a new method of financial extraction." The targeting of sensitive cryptocurrency data by threat actors was recently echoed by the Microsoft 365 Defender Research Team, which warned about the emerging threat of cryware wherein private keys, seed phrases, and wallet addresses are plundered with the goal of siphoning virtual currencies by means of fraudulent transfers.

An unofficial security patch has been made available for a new Windows zero-day vulnerability in the Microsoft Support Diagnostic Tool, even as the Follina flaw continues to be exploited in the wild. The issue - referenced as DogWalk - relates to a path traversal flaw that can be exploited to stash a malicious executable file to the Windows Startup folder when a potential target opens a specially crafted ".

Attackers aren't slowing down; in fact, ransomware attacks are almost ubiquitous. In nearly every case, the victim had already been compromised by one or more threats on the way to becoming a ransomware victim.
A new wave of phishing campaigns has been observed spreading a previously documented malware called SVCReady. "The malware is notable for the unusual way it is delivered to target PCs - using shellcode hidden in the properties of Microsoft Office documents," Patrick Schläpfer, a threat analyst at HP, said in a technical write-up.

Parrot TDS was documented in April 2022 by Czech cybersecurity company Avast, noting that the PHP script had ensnared web servers hosting more than 16,500 websites to act as a gateway for further attack campaigns. The goal of the JavaScript code is to kick-start the second phase of the attack, which is to execute a PHP script that's already deployed on the ever and is designed to gather information about a site visitor and transmit the details to a remote server.
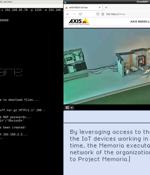
Called Ransomware for IoT or R4IoT by Forescout, it's a "Novel, proof-of-concept ransomware that exploits an IoT device to gain access and move laterally in an IT network and impact the OT network." This potential pivot is based on the rapid growth in the number of IoT devices as well as the convergence of IT and OT networks in organizations.