Security News

Quantum computing has surged in popularity recently, with its revolutionary computational capabilities transforming the technology sector. In this Help Net Security video, Vanesa Diaz, CEO at LuxQuanta, talks about how precautions must be taken ahead of this new quantum age, where cybersecurity solutions require significant attention and developments to ensure the protection and security of data.

Research conducted by Fujitsu suggests there is no need to panic about quantum computers being able to decode encrypted data - this is unlikely to happen in the near future, it claims. Fujitsu said it ran trials using its 39-qubit quantum simulator hardware to assess how difficult it would be for quantum computers to crack data encrypted with the RSA cipher, using a Shor's algorithm approach.

The growing interest in quantum is translating into spending, demonstrated by 71% of quantum-adopting enterprises surveyed having current quantum computing budgets of more than $1 million. Interestingly, nearly 30% of respondents that have adopted or plan to adopt quantum computing expect to see a competitive advantage due to quantum computing within the next 12 months.

The paper, titled "Factoring integers with sublinear resources on a superconducting quantum processor," suggests that the application of Claus Peter Schnorr's recent factoring algorithm, in conjunction with a quantum approximate optimization algorithm, can break asymmetric RSA-2048 encryption using a non-fault tolerant quantum computer with only 372 physical quantum bits or qubits. The speculation has been that orders of magnitude more qubits, in conjunction with robust error correction at scale, may allow future quantum computers to run Peter Schor's algorithm - not to be confused with the similarly named Schnorr - quickly, on very large numbers, thereby breaking RSA encryption.

We have long known from Shor's algorithm that factoring with a quantum computer is easy. What the researchers have done is combine classical lattice reduction factoring techniques with a quantum approximate optimization algorithm.

Remember quantum computing, and the quantum computers that make it possible? Quantum computing enthusiasts claim the performance improvements will be so dramatic that encryption keys that could once comfortably have held out against even the richest and most antagonistic governments in the world for decades.

Cloudflare is the first major internet infrastructure provider to support post-quantum cryptography for all customers, which, in theory, should protect data if quantum computing ever manages to break today's encryption technologies. Starting today all websites and APIs served through Cloudflare support post-quantum TLS based on the Kyber hybrid key agreement.

Quantum Builder lets attackers to create malicious Microsoft Windows LNK shortcuts. Quantum Builder has been linked to the advanced persistent threat gang Lazarus Group, based on shared tactics, techniques, and procedures and overlaps in source code, but they can't with any confidence attribute the current campaign to Lazarus or any particular threat group.
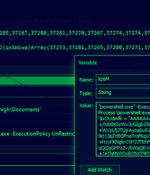
A recently discovered malware builder called Quantum Builder is being used to deliver the Agent Tesla remote access trojan. Sold on the dark web for €189 a month, Quantum Builder is a customizable tool for generating malicious shortcut files as well as HTA, ISO, and PowerShell payloads to deliver next-stage malware on the targeted machines, in this case Agent Tesla.

The Emotet malware is now being leveraged by ransomware-as-a-service groups, including Quantum and BlackCat, after Conti's official retirement from the threat landscape this year. Emotet started off as a banking trojan in 2014, but updates added to it over time have transformed the malware into a highly potent threat that's capable of downloading other payloads onto the victim's machine, which would allow the attacker to control it remotely.