Security News

A zero-day security flaw in Telegram's mobile app for Android called EvilVideo made it possible for attackers to malicious files disguised as harmless-looking videos. The exploit appeared for sale...

Threat actors are taking advantage of the massive popularity of the Hamster Kombat game, targeting players with fake Android and Windows software that install spyware and information-stealing...

Russian-linked malware was used in a January 2024 cyberattack to cut off the heating of over 600 apartment buildings in Lviv, Ukraine, for two days during sub-zero temperatures. [...]

CrowdStrike is warning that a fake recovery manual to repair Windows devices is installing a new information-stealing malware called Daolpu. [...]

Organizations in Taiwan and a U.S. non-governmental organization based in China have been targeted by a Beijing-affiliated state-sponsored hacking group called Daggerfly using an upgraded set of malware tools. Daggerfly, also known by the names Bronze Highland and Evasive Panda, was previously observed using the MgBot modular malware framework in connection with an intelligence-gathering mission aimed at telecom service providers in Africa.

Cybersecurity researchers have discovered what they say is the ninth Industrial Control Systems (ICS)-focused malware that has been used in a disruptive cyber attack targeting an energy company in...

The Computer Emergency Response Team of Ukraine has alerted of a spear-phishing campaign targeting a scientific research institution in the country with malware known as HATVIBE and CHERRYSPY. The agency attributed the attack to a threat actor it tracks under the name UAC-0063, which was previously observed targeting various government entities to gather sensitive information using keyloggers and backdoors. Opening the document and enabling macros results in the execution of an encoded HTML Application named HATVIBE, which sets up persistence on the host using a scheduled task and paves the way for a Python backdoor codenamed CHERRYSPY, which is capable of running commands issued by a remote server.
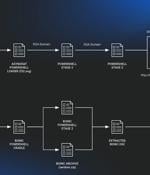
The JavaScript downloader malware known as SocGholish is being used to deliver a remote access trojan called AsyncRAT as well as a legitimate open-source project called BOINC. BOINC, short for Berkeley Open Infrastructure Network Computing Client, is an open-source "Volunteer computing" platform maintained by the University of California with an aim to carry out "Large-scale distributed high-throughput computing" using participating home computers on which the app is installed. The JavaScript downloader, in this case, activates two disjointed chains, one that leads to the deployment of a fileless variant of AsyncRAT and the other resulting in the BOINC installation.

ESET Research has discovered a sophisticated Chinese browser injector: a signed, vulnerable, ad-injecting driver from a mysterious Chinese company. An attacker with a non-privileged account could leverage the vulnerable driver to obtain SYSTEM privileges or inject libraries into remote processes to cause further damage, all while using a legitimate and signed driver.

Threat actors are exploiting the massive business disruption from CrowdStrike's glitchy update on Friday to target companies with data wipers and remote access tools. [...]