Security News

It's not my intention to be alarmist about the Log4j vulnerability, known as Log4Shell, but this one is pretty bad. First of all, Log4j is a ubiquitous logging library that is very widely used by millions of computers. Second, the director of the U.S. Cybersecurity & Infrastructure Security Agency says this is the most serious vulnerability.
An Iranian state-sponsored actor has been observed scanning and attempting to abuse the Log4Shell flaw in publicly-exposed Java applications to deploy a hitherto undocumented PowerShell-based modular backdoor dubbed "CharmPower" for follow-on post-exploitation. Log4Shell aka CVE-2021-44228 concerns a critical security vulnerability in the popular Log4j logging library that, if successfully exploited, could lead to remote execution of arbitrary code on compromised systems.

Hackers believed to be part of the Iranian APT35 state-backed group has been observed leveraging Log4Shell attacks to drop a new PowerShell backdoor. As part of their research, the analysts also spotted something new in the form of a PowerShell modular backdoor named 'CharmPower.

With the last month of 2021 dominated by the log4J vulnerabilities discovery, publication, and patches popping up in rapid succession, odds are you have patched your system against Log4J exploitation attempts. 3 - The odds of missing at least one instance of Log4J are high: All version of Log4J from the September 2013 V2.0-beta9 onwards carry those vulnerabilities.

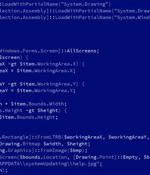
The Night Sky ransomware gang has started to exploit the critical CVE-2021-44228 vulnerability in the Log4j logging library, also known as Log4Shell, to gain access to VMware Horizon systems. Spotted in late December 2021 by security researcher MalwareHunterTeam, Night Sky ransomware focuses on locking enterprise networks.

There have been millions of downloads of outdated, vulnerable Log4j versions despite the emergence of a serious security hole in December 2021, according to figures compiled by the firm that runs Apache Maven's Central Repository. Tracked as CVE-2021-44228 aka Log4shell, the original vulnerability affected version 2.14 and earlier of the 2.x branch of the Apache logging utility.

Check Point Research said Africa had the highest amount with an average of 1,582 per week per organization. For 2021 as a whole, the number of cyberattacks against corporate networks soared by 50% from the previous year, cyber threat intelligence provider Check Point Research said in a report released on Monday.
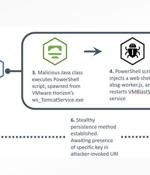
The digital security team at the U.K. National Health Service has raised the alarm on active exploitation of Log4Shell vulnerabilities in unpatched VMware Horizon servers by an unknown threat actor to drop malicious web shells and establish persistence on affected networks for follow-on attacks. "The attack likely consists of a reconnaissance phase, where the attacker uses the Java Naming and Directory InterfaceTM via Log4Shell payloads to call back to malicious infrastructure," the non-departmental public body said in an alert.

Besides the difficulty of tracking down all instances of the ubiquitous Apache logging library, the job of patching the flaws has been further complicated for many agencies by end-of-life and end-of-support systems connected to the network. Due to network-connected EoL and EoS systems: an issue that's further complicated by pandemic-wrought supply chain delays and remote-work issues.

Researchers discovered a bug related to the Log4J logging library vulnerability, which in this case opens the door for an adversary to execute remote code on vulnerable systems. JFrog security discovered the flaw and rated critical in the context of the H2 Java database console, a popular open-source database, according to a Thursday blog post by researchers.