Security News

Usual three-week window to address significant risks to federal agencies applies The US Cybersecurity and Infrastructure Security Agency (CISA) says vulnerabilities in Fortinet and Ivanti products...

The U.S. Cybersecurity and Infrastructure Security Agency (CISA) on Wednesday added a critical security flaw impacting Fortinet products to its Known Exploited Vulnerabilities (KEV) catalog,...


That would explain this 440GB leak, then Fortinet has admitted that bad actors accessed cloud-hosted data about its customers, but insisted it was a "limited number" of files. The question is: how...

Fortinet, a leading cybersecurity company, has confirmed a data breach after a threat actor, using the alias "Fortibitch," claimed to have stolen 440GB of data from its Microsoft SharePoint server hosted on Azure. Fortinet provides secure networking products like firewalls, routers, and VPNs, alongside services like SIEM, EDR/XDR, and consulting. The breach was first reported on a hacking forum, where the attacker shared credentials to an S3 bucket allegedly containing the stolen files. While the threat actor attempted to extort Fortinet, the company refused to pay the ransom.Fortinet has acknowledged that a limited amount of customer data was stolen from a third-party cloud-based file drive. However, the company did not disclose the exact number of customers affected or the type of compromised data. Fortinet later updated its website, clarifying that less than 0.3% of its customer base was impacted and that no malicious activity had been directed toward these customers as a result of the breach. Additionally, Fortinet assured that the incident did not involve ransomware, data encryption, or unauthorized access to its corporate network.

As two top NGFWs, Fortinet FortiGate seems to best fit small businesses, while Palo Alto works best for larger organizations. Find out in our comparison below.

The China-nexus cyber espionage actor linked to the zero-day exploitation of security flaws in Fortinet, Ivanti, and VMware devices has been observed utilizing multiple persistence mechanisms in...

State-sponsored threat actors backed by China gained access to 20,000 Fortinet FortiGate systems worldwide by exploiting a known critical security flaw between 2022 and 2023, indicating that the...

Security researchers have released a proof-of-concept exploit for a maximum-severity vulnerability in Fortinet's security information and event management solution, which was patched in February.On Tuesday, over three months after Fortinet released security updates to patch this security flaw, Horizon3's Attack Team shared a proof-of-concept exploit and published a technical deep-dive.
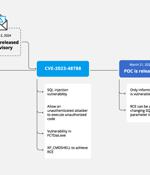
Cybersecurity researchers have discovered a new campaign that's exploiting a recently disclosed security flaw in Fortinet FortiClient EMS devices to deliver ScreenConnect and Metasploit Powerfun...