Security News

In this article, I'll be running down a quick list of the five best VPNs for Android in 2024. While all the VPNs on this list secure your internet connection on your Android device, not all of them share the same set of features and pricing.

The GrapheneOS team behind the privacy and security-focused Android-based operating system with the same name is suggesting that Android should introduce an auto-reboot feature to make exploitation of firmware flaws more difficult. The project revealed that it recently reported firmware vulnerabilities in the Android operating system that impact Google Pixel and Samsung Galaxy phones, which could be exploited to steal data and spy on users when the device is not at rest.

Patch Tuesday Microsoft rang in the New Year with a relatively calm Patch Tuesday: Just 49 Windows security updates including fixes for two critical-rated bugs, plus four high-severity Chrome flaws in Microsoft Edge. "And while it's listed as exploitation less likely, because Hyper-V runs as the highest privileges in a computer, it is worth thinking about patching," Ben McCarthy, lead cyber security engineer at Immersive Labs told The Register.

Users of the Firefox browser for Android have been reporting that they are seeing a blank page when trying to load the main Google Search site. A report of the issue on GitHub confirms that the problem is reproducible on Firefox Mobile 121.0 for Android 13 and additional tests indicate the same behavior on Firfox Nightly 123 and all versions starting v65.

About Bruce Schneier I am a public-interest technologist, working at the intersection of security, technology, and people. I've been writing about security issues on my blog since 2004, and in my monthly newsletter since 1998.

Japanese game developer Ateam has proven that a simple Google Drive configuration mistake can result in the potential but unlikely exposure of sensitive information for nearly one million people over a period of six years and eight months. Setting Google Drive to "Anyone with the link can view" makes it viewable only to those with the exact URL, typically reserved for collaboration between people working with non-sensitive data.

A previously unknown Android backdoor named 'Xamalicious' has infected approximately 338,300 devices via malicious apps on Google Play, Android's official app store. Even though the apps have since been removed from Google Play, users who installed them since mid-2020 might still carry active Xamalicious infections on their phones, requiring manual scans and cleanup.

A new Android backdoor has been discovered with potent capabilities to carry out a range of malicious actions on infected devices. Dubbed Xamalicious by the McAfee Mobile Research Team, the...

Cybersecurity company ESET released its H2 2023 threat report, and we're highlighting three particularly interesting topics in it: the abuse of the ChatGPT name by cybercriminals, the rise of the Lumma Stealer malware and the Android SpinOk SDK spyware. In the second half of 2023, ESET has blocked 650,000 attempts to access malicious domains whose names include "Chatgpt" or similar string in an apparent reference to the ChatGPT chatbot.
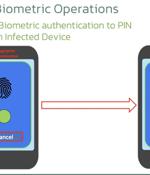
Cybersecurity researchers have discovered an updated version of an Android banking malware called Chameleon that has expanded its targeting to include users in the U.K. and Italy. "Representing a...