Security News

A Mirai botnet variant dubbed Aquabot has been observed actively attempting to exploit a medium-severity security flaw impacting Mitel phones in order to ensnare them into a network capable of...

A new variant of the Mirai-based botnet malware Aquabot has been observed actively exploiting CVE-2024-41710, a command injection vulnerability in Mitel SIP phones. [...]

And now you won't stop calling me, I'm kinda busy A new variant of the Mirai-based malware Aquabot is actively exploiting a vulnerability in Mitel phones to build a remote-controlled botnet,...

3 CVEs added to CISA's catalog Cybercriminals are actively exploiting two vulnerabilities in Mitel MiCollab, including a zero-day flaw – and a critical remote code execution vulnerability in...

CISA has added Mitel MiCollab (CVE-2024-41713, CVE-2024-55550) and Oracle WebLogic Server (CVE-2020-2883) vulnerabilities to its Known Exploited Vulnerabilities (KEV) catalog. The Mitel MiCollab...

The U.S. Cybersecurity and Infrastructure Security Agency (CISA) on Tuesday added three flaws impacting Mitel MiCollab and Oracle WebLogic Server to its Known Exploited Vulnerabilities (KEV)...

CISA has warned U.S. federal agencies to secure their systems against critical vulnerabilities in Oracle WebLogic Server and Mitel MiCollab systems that are actively exploited in attacks. [...]

Still unpatched 100+ days later, watchTowr says A zero-day arbitrary file read vulnerability in Mitel MiCollab can be chained with a now-patched critical bug in the same platform to give attackers...
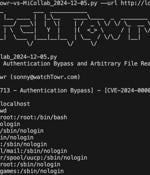
Cybersecurity researchers have released a proof-of-concept (PoC) exploit that strings together a now-patched critical security flaw impacting Mitel MiCollab with an arbitrary file read zero-day,...

A zero-day vulnerability in the Mitel MiCollab enterprise collaboration suite can be exploited to read files containing sensitive data, watchTowr researcher Sonny Macdonald has disclosed, and...