Security News

The Glupteba malware botnet has sprung back into action, infecting devices worldwide after its operation was disrupted by Google almost a year ago. Nozomi now reports that blockchain transactions, TLS certificate registrations, and reverse engineering Glupteba samples show a new, large-scale Glupteba campaign that started in June 2022 and is still ongoing.

A new cross-platform malware botnet named 'MCCrash' is infecting Windows, Linux, and IoT devices to conduct distributed denial of service attacks on Minecraft servers. "Our analysis of the DDoS botnet revealed functionalities specifically designed to target private Minecraft Java servers using crafted packets, most likely as a service sold on forums or darknet sites," explains the new report by Microsoft.
A previously undocumented Android malware campaign has been observed leveraging money-lending apps to blackmail victims into paying up with personal information stolen from their devices. The money lending applications, instead, are available through unofficial app stores or sideloaded to the phones via smishing, compromised websites, rogue ads, or social media campaigns.

A hacking group tracked as MirrorFace has been targeting Japanese politicians for weeks before the House of Councilors election in July 2022, using a previously undocumented credentials stealer named 'MirrorStealer. The hackers deployed the new information-stealing malware along with the group's signature backdoor, LODEINFO, which communicated with a C2 server known to belong to APT10 infrastructure.
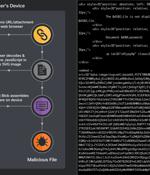
Phishing campaigns involving the Qakbot malware are using Scalable Vector Graphics images embedded in HTML email attachments. The new distribution method was spotted by Cisco Talos, which said it identified fraudulent email messages featuring HTML attachments with encoded SVG images that incorporate HTML script tags.

Another month, another Microsoft Patch Tuesday, another 48 patches, another two zero-days. An astonishing tale about a bunch of rogue actors who tricked Microsoft itself into giving their malicious code an official digital seal of approval.

QBot malware phishing campaigns have adopted a new distribution method using SVG files to perform HTML smuggling that locally creates a malicious installer for Windows. This attack is made through embedded SVG files containing JavaScript that reassemble a Base64 encoded QBot malware installer that is automatically downloaded through the target's browser.

An active malware campaign is targeting the Python Package Index and npm repositories for Python and JavaScript with typosquatted and fake modules that deploy a ransomware strain, marking the latest security issue to affect software supply chains. According to Phylum, the rogue packages embed source code that retrieves Golang-based ransomware binary from a remote server depending on the victim's operating system and microarchitecture.

A previously undocumented Python backdoor targeting VMware ESXi servers has been spotted, enabling hackers to execute commands remotely on a compromised system. VMware ESXi is a virtualization platform commonly used in the enterprise to host numerous servers on one device while using CPU and memory resources more effectively.

According to Cisco Talos, TrueBot malware now collects Active Directory information, which means it targets businesses with larger IT resources. In addition to targeting larger organizations, the malware is experimenting with new delivery methods: Netwrix Auditor bundled with the Raspberry Robin malware.