Security News
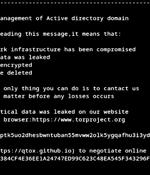
Cybersecurity researchers have shed light on a Linux variant of a relatively new ransomware strain called Helldown, suggesting that the threat actors are broadening their attack focus. "Helldown...

Event The security landscape is constantly shifting. If you're running Linux, staying ahead may rely on understanding the challenges - and opportunities - unique to Linux environments.…

Cybersecurity researchers have flagged a new malware campaign that infects Windows systems with a Linux virtual instance containing a backdoor capable of establishing remote access to the...

Unknown attackers are trying to trick Windows users into spinning up a custom Linux virtual machine (VM) with a pre-configured backdoor, Securonix researchers have discovered. The campaign The...

A new phishing campaign dubbed 'CRON#TRAP' infects Windows with a Linux virtual machine that contains a built-in backdoor to give stealthy access to corporate networks. [...]

The latest generations of Intel processors, including Xeon chips, and AMD's older Zen 1, Zen 1+, and Zen 2 microarchitectures on Linux are vulnerable to new speculative execution attacks that...

North Korean threat actors have been observed using a Linux variant of a known malware family called FASTCash to steal funds as part of a financially-motivated campaign. The malware is "installed...

North Korean hackers are using a new Linux variant of the FASTCash malware to infect the payment switch systems of financial institutions and perform unauthorized cash withdrawals. [...]

An automated scanner has been released to help security professionals scan environments for devices vulnerable to the Common Unix Printing System (CUPS) RCE flaw tracked as CVE-2024-47176. [...]

Thousands of Linux systems are likely infected with the highly elusive and persistent “perfctl” (or “perfcc“) cryptomining malware and many others still could be at risk of getting compromised,...