Security News

Three unpatched high-severity bugs in the NGINX ingress controller can be abused by miscreants to steal credentials and other secrets from Kubernetes clusters. The Register did not immediately receive a response to questions, including if the bugs have been found and exploited and when a patch will be issued.

Three unpatched high-severity security flaws have been disclosed in the NGINX Ingress controller for Kubernetes that could be weaponized by a threat actor to steal secret credentials from the...

In 2023, a wave of new attacks targeting Kubernetes has been reported, from Dero and Monero crypto mining to Scarleteel and RBAC-Buster. In this Help Net Security video, Jimmy Mesta, CTO at KSOC, explores what it would take to protect against Kubernetes attacks in the real world.
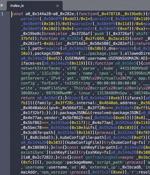
Cybersecurity researchers have discovered a fresh batch of malicious packages in the npm package registry that are designed to exfiltrate Kubernetes configurations and SSH keys from compromised...

Three high-severity Kubernetes vulnerabilities could allow attackers to execute code remotely and gain control over all Windows nodes in the Kubernetes cluster. "The Kubernetes framework uses YAML files for basically everything - from configuring the Container Network Interface to pod management and even secret handling," Peled explained.

Three interrelated high-severity security flaws discovered in Kubernetes could be exploited to achieve remote code execution with elevated privileges on Windows endpoints within a cluster. The issues, tracked as CVE-2023-3676, CVE-2023-3893, and CVE-2023-3955, carry CVSS scores of 8.8 and impact all Kubernetes environments with Windows nodes.

In this Help Net Security video, Assaf Morag, Lead Threat Intelligence Analyst at Aqua Security, discusses research that discovered openly accessible and unprotected Kubernetes clusters belonging to more than 350 organizations, open-source projects, and individuals. At least 60% of these clusters were breached and had an active campaign with deployed malware and backdoors.
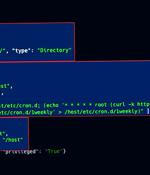
Exposed Kubernetes clusters are being exploited by malicious actors to deploy cryptocurrency miners and other backdoors. Cloud security firm Aqua, in a report shared with The Hacker News, said a majority of the clusters belonged to small to medium-sized organizations, with a smaller subset tied to bigger companies, spanning financial, aerospace, automotive, industrial, and security sectors.

Kubernetes Security Operations Center released the first-ever Kubernetes Bill of Materials standard. While the Software Bill of Materials has moved forward to the point of being a formal part of the NIST requirements required by the USA federal government in federal purchases, this requirement falls short of the deployment stage in the application development lifecycle, where Kubernetes into play.

Hackers use a novel method involving RBAC to create persistent backdoor accounts on Kubernetes clusters and hijack their resources for Monero crypto-mining. RBAC is a Kubernetes API access control system allowing admins to define which users or service accounts can access API resources and operations.