Security News

Proof-of-concept exploit code has been publicly released for vulnerabilities in Juniper SRX firewalls that, when chained, can allow unauthenticated attackers to gain remote code execution in Juniper's JunOS on unpatched devices.Juniper disclosed four medium-severity bugs in its EX switches and SRX firewalls and released security patches two weeks ago.

Any clues as to what makes up the structure of a password is very helpful to hackers. We'll walk through how hackers take advantage of four of the most common password mistakes users make, as well as ways to strengthen your Active Directory against these risks.

Proof-of-concept exploit code is now available for a critical Ivanti Sentry authentication bypass vulnerability that enables attackers to execute code remotely as root on vulnerable systems. Successful exploitation can let them run system commands or write files onto systems running Ivanti Sentry versions 9.18 and prior.
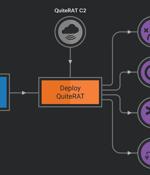
The North Korea-linked threat actor known as Lazarus Group has been observed exploiting a now-patched critical security flaw impacting Zoho ManageEngine ServiceDesk Plus to distribute a remote access trojan called such as QuiteRAT. Targets include internet backbone infrastructure and healthcare entities in Europe and the U.S., cybersecurity company Cisco Talos said in a two-part analysis published today. What's more, a closer examination of the adversary's recycled attack infrastructure in its cyber assaults on enterprises has led to the discovery of a new threat dubbed CollectionRAT. The fact that the Lazarus Group continues to rely on the same tradecraft despite those components being well-documented over the years underscores the threat actor's confidence in their operations, Talos pointed out.

The North Korean state-backed hacker group tracked as Lazarus has been exploiting a critical vulnerability in Zoho's ManageEngine ServiceDesk to compromise an internet backbone infrastructure provider and healthcare organizations. Cisco Talos researchers observed attacks against UK internet firms in early 2023, when Lazarus leveraged an exploit for CVE-2022-47966, a pre-authentication remote code execution flaw affecting multiple Zoho ManageEngine products.

In this Help Net Security video, Andy Hornegold, Product Lead at Intruder, dives into API security and explores how several recent high-profile breaches were caused by simple failings - which didn't require sophisticated security to prevent. The number of APIs is increasing year on year as more organizations are building APIs to facilitate automation.

The Cuba ransomware gang was observed in attacks targeting critical infrastructure organizations in the United States and IT firms in Latin America, using a combination of old and new tools. BlackBerry's Threat Research and Intelligence team, which spotted the latest campaign in early June 2023, reports that Cuba now leverages CVE-2023-27532 to steal credentials from configuration files.
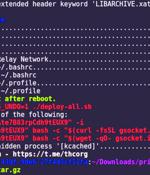
A new, financially motivated operation dubbed LABRAT has been observed weaponizing a now-patched critical flaw in GitLab as part of a cryptojacking and proxyjacking campaign. Proxyjacking allows the attacker to rent the compromised host out to a proxy network, making it possible to monetize the unused bandwidth.

Cybersecurity researchers have documented a novel post-exploit persistence technique on iOS 16 that could be abused to fly under the radar and main access to an Apple device even when the victim believes it is offline. The method "Tricks the victim into thinking their device's Airplane Mode works when in reality the attacker has planted an artificial Airplane Mode which edits the UI to display Airplane Mode icon and cuts internet connection to all apps except the attacker application," Jamf Threat Labs researchers Hu Ke and Nir Avraham said in a report shared with The Hacker News.

A team of researchers from UC Irvine and Tsinghua University has developed a new powerful cache poisoning attack named 'MaginotDNS,' that targets Conditional DNS resolvers and can compromise entire TLDs top-level domains. The concept of DNS cache poisoning is injecting forged answers into the DNS resolver cache, causing the server to direct users who enter a domain to incorrect IP addresses, potentially leading them to malicious websites without their knowledge.