Security News

The threat actors behind the BlackByte ransomware group have been observed likely exploiting a recently patched security flaw impacting VMware ESXi hypervisors, while also leveraging various...

Why a strong patch management strategy is essential for reducing business riskIn this Help Net Security interview, Eran Livne, Senior Director of Product Management, Endpoint Remediation at Qualys and Thomas Scheffler, Security Operations Manager of Cintas Corporation, discuss their experiences with automated patch management. These risks are driven by heightened cybersecurity threats, evolving regulations, and increased public awareness of security breaches.

A vulnerability in the ESXi hypervisor was patched by VMware last week, but Microsoft has revealed that it has already been exploited by ransomware groups to gain administrative permissions. The vulnerability affects ESXi versions 7.0 and 8.0 and VMware Cloud Foundation versions 4.x and 5.x., but patches were only rolled out for ESXi 8.0 and VMware Cloud Foundation 5.x. It has a relatively low CVSS severity score of 6.8.

CISA has ordered U.S. Federal Civilian Executive Branch agencies to secure their servers against a VMware ESXi authentication bypass vulnerability exploited in ransomware attacks. Broadcom subsidiary VMware fixed this flaw discovered by Microsoft security researchers on June 25 with the release of ESXi 8.0 U3. CVE-2024-37085 allows attackers to add a new user to the 'ESX Admins' group-not present by default but can be added after gaining high privileges on the ESXi hypervisor-which will automatically be assigned full administrative privileges.

CVE-2024-37085 only carries a 6.8 CVSS rating, but has been used as a post-compromise technique by many of the world's most high-profile ransomware groups and their affiliates, including Black Basta, Akira, Medusa, and Octo Tempest/Scattered Spider. The vulnerability allows attackers who have the necessary privileges to create AD groups - which isn't necessarily an AD admin - to gain full control of an ESXi hypervisor.

Ransomware operators have been leveraging CVE-2024-37085, an authentication bypass vulnerability affecting Active Directory domain-joined VMware ESXi hypervisors, to gain full administrative access to them and encrypt their file system."ESXi is a bare-metal hypervisor that is installed directly onto a physical server and provides direct access and control of underlying resources. ESXi hypervisors host virtual machines that may include critical servers in a network," Microsoft's threat analysts explained.
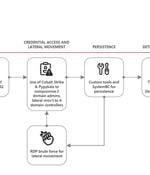
A recently patched security flaw impacting VMware ESXi hypervisors has been actively exploited by "Several" ransomware groups to gain elevated permissions and deploy file-encrypting malware. "A malicious actor with sufficient Active Directory permissions can gain full access to an ESXi host that was previously configured to use AD for user management by re-creating the configured AD group after it was deleted from AD," Broadcom-owned VMware noted in an advisory released in late June 2024.

Microsoft warned today that ransomware gangs are actively exploiting a VMware ESXi authentication bypass vulnerability in attacks. Ransomware groups have focused on creating lockers dedicated to encrypting ESXi VMs rather than targeting specific ESXi vulnerabilities that would provide them a quicker way of acquiring and maintaining access to a victim's hypervisors.

Play ransomware is the latest ransomware gang to start deploying a dedicated locker for encrypting Linux devices and specifically targeting VMware ESXi virtual machines. [...]
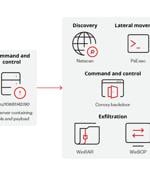
Cybersecurity researchers have discovered a new Linux variant of a ransomware strain known as Play that's designed to target VMWare ESXi environments. Manufacturing, professional services, construction, IT, retail, financial services, transportation, media, legal services, and real estate are some of the top industries affected by the Play ransomware during the time period.