Security News

China appears to be entering a raging cyber-espionage battle that's grown in line with Russia's unprovoked attack on Ukraine, deploying advanced malware on the computer systems of Russian officials. China has tried to play a neutral role since Russia began its invasion of Ukraine on February 24, with government officials saying they want to see a peaceful resolution.

Trouble is brewing over moves by Taiwan to prevent China from gaining access to its chip technology, as the island nation proposes tougher laws to deter the leaking of trade secrets outside the country. China has reportedly hit back after Taiwanese Premier Su Tseng-chang called this week for a speedier introduction of legislation designed to protect the local semiconductor industry from what it sees as Chinese industrial espionage.
A Chinese state-backed advanced persistent threat group known for singling out Japanese entities has been attributed to a new long-running espionage campaign targeting new geographies, suggesting a "Widening" of the threat actor's targeting. "Victims in this Cicada campaign include government, legal, religious, and non-governmental organizations in multiple countries around the world, including in Europe, Asia, and North America," researchers from the Symantec Threat Hunter Team, part of Broadcom Software, said in a report shared with The Hacker News.

The Daxin malware is taking aim at hardened government networks around the world, according to researchers, with the goal of cyberespionage. "Daxin malware is a highly sophisticated rootkit backdoor with complex, stealthy command-and-control functionality that enabled remote actors to communicate with secured devices not connected directly to the internet," warned CISA, in a Monday alert.
A previously undocumented espionage tool has been deployed against selected governments and other critical infrastructure targets as part of a long-running espionage campaign orchestrated by China-linked threat actors since at least 2013. Broadcom's Symantec Threat Hunter team characterized the backdoor, named Daxin, as a technologically advanced malware, allowing the attackers to carry out a variety of communications and information-gathering operations aimed at entities in the telecom, transportation, and manufacturing sectors that are of strategic interest to China.

The United States' National Security Division will wind up its "China Initiative" - an effort to combat what then-attorney general Jeff Sessions described in 2018 as "Systematic and calculated threats" posed by Beijing-backed economic espionage. "We have heard concerns from the civil rights community that the 'China Initiative' fueled a narrative of intolerance and bias," Olsen stated in a speech delivered at the National Security Institute and George Mason University.

The politically motivated Moses Staff hacker group has been observed using a custom multi-component toolset with the goal of carrying out espionage against its targets as part of a new campaign that exclusively singles out Israeli organizations. First publicly documented in late 2021, Moses Staff is believed to be sponsored by the Iranian government, with attacks reported against entities in Israel, Italy, India, Germany, Chile, Turkey, the U.A.E., and the U.S. Earlier this month, the hacker collective was observed incorporating a previously undocumented remote access trojan called "StrifeWater" that masquerades as the Windows Calculator app to evade detection.

An advanced persistent threat group with ties to Iran has refreshed its malware toolset to include a new backdoor dubbed Marlin as part of a long-running espionage campaign that started in April 2018. Slovak cybersecurity company ESET attributed the attacks - code named Out to Sea - to a threat actor called OilRig, while also conclusively connecting its activities to a second Iranian group tracked under the name Lyceum.
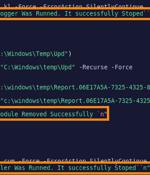
An advanced persistent threat group with links to Iran has updated its malware toolset to include a novel PowerShell-based implant called PowerLess Backdoor, according to new research published by Cybereason. The Boston-headquartered cybersecurity company attributed the malware to a hacking group known as Charming Kitten, while also calling out the backdoor's evasive PowerShell execution.

Cybersecurity researchers on Monday said they uncovered evidence of attempted attacks by a Russia-linked hacking operation targeting a Ukrainian entity in July 2021. Broadcom-owned Symantec, in a new report published Monday, attributed the attacks to an actor tracked as Gamaredon, a cyber-espionage collective known to be active since at least 2013.