Security News

A financially motivated threat actor of Indonesian origin has been observed leveraging Amazon Web Services Elastic Compute Cloud instances to carry out illicit crypto mining operations. Cloud security company's Permiso P0 Labs, which first detected the group in November 2021, has assigned it the moniker GUI-vil.
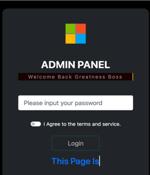
A new phishing-as-a-service platform named Greatness has been leveraged by cybercriminals to target business users of the Microsoft 365 cloud service since at least mid-2022, effectively lowering the bar to entry for phishing attacks. "Greatness, for now, is only focused on Microsoft 365 phishing pages, providing its affiliates with an attachment and link builder that creates highly convincing decoy and login pages," Cisco Talos researcher Tiago Pereira said.

Bot attacks were previously seen as relatively inconsequential type of online fraud, and that mentality has persisted even as threat actors have gained the ability to cause significant damage to revenue and brand reputation, according to HUMAN. Bad bot traffic. Bad bot traffic overall increased even as people spent less time online.

The study is built upon 10 million posts on encrypted platforms and other kinds of data dredged up from the deep, dark and clear web. Across the dark web onion sites, the total number of forum posts and replies decreased by 13% between 2021 and 2022, dropping from over 91.7 million to around 79.1 million.

Malware developers have created a thriving market promising to add malicious Android apps to Google Play for $2,000 to $20,000, depending on the type of malicious behavior cyber criminals request. The exact price for these services is negotiated on a case-by-case basis on hacker forums or Telegram channels, allowing cybercriminals to customize malicious Android apps with their own malware or functionality.

"The most popular application categories to hide malware and unwanted software include cryptocurrency trackers, financial apps, QR-code scanners, and even dating apps," Kaspersky said in a new report based on messages posted on online forums between 2019 and 2023. Dropper apps are the primary means for threat actors looking to sneak malware via the Google Play Store.

People reveal more personal information when you ask them the same questions a second time - according to new research from the University of East Anglia. The research team say that understanding why people disclose personal data could help inform measures to address the problem.
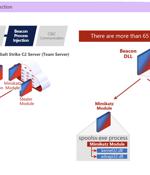
Microsoft said it teamed up with Fortra and Health Information Sharing and Analysis Center to tackle the abuse of Cobalt Strike by cybercriminals to distribute malware, including ransomware. While Cobalt Strike, developed and maintained by Fortra, is a legitimate post-exploitation tool used for adversary simulation, illegal cracked versions of the software have been weaponized by threat actors over the years.

Resecurity has recently identified the STYX Innovation Marketplace, a new cybercriminal e-commerce platform with a specialized focus on financial fraud and money laundering. This platform is specifically designed to facilitate financial crime, providing cybercriminals with a range of services, including stolen financial data, credit card information, forged documents, money laundering services, victim reconnaissance 'lookups', and more.

The fake crimeware-as-a-service offerings that the NCA pretends to operate are so-called booters, also known as stressers, also known as DDoSsers, where DDoS is short for distributed denial of service. In contrast, DDoS attacks are usually much less sophisticated, making them easier for technically inexperienced crooks to take part in, but much more natural-looking, making them harder even for technically experienced defenders to stop.