Security News

A critical vulnerability that affects Cisco Enterprise NFV Infrastructure Software has been patched and Cisco is urging enterprise admins to quickly upgrade to a fixed version, as proof-of-concept exploit code is already available. The bug could be exploited by remote attackers to bypass authentication and log in to an affected device as an administrator.

Cisco has patched a near-max critical bug in its NFVIS software for which there's a publicly available proof-of-concept exploit. On Wednesday, Cisco released patches for the flaw - an authentication bypass vulnerability in Enterprise NFV Infrastructure Software that's tracked as CVE-2021-34746.

Cisco has addressed an almost maximum severity authentication bypass Enterprise NFV Infrastructure Software vulnerability with public proof-of-concept exploit code.CVE-2021-34746 is caused by incomplete validation of user-supplied input passed to an authentication script during the sign-in process which allows unauthenticated, remote attackers to log into unpatched device as an administrator.

Cyber attacks against critical national infrastructure are escalating. The most frequently-discussed aspect of critical infrastructure events are availability impacts: stopping or interrupting a process or organization.

A critical security vulnerability in Microsoft's Azure cloud database platform - Cosmos DB - could have allowed full remote takeover of accounts, with admin rights to read, write and delete any information to a database instance. "Azure Cosmos DB built-in Jupyter Notebooks are directly integrated into the Azure portal and your Azure Cosmos DB accounts, making them convenient and easy to use," according to Microsoft's documentation.

Microsoft has warned thousands of Azure customers that a now-fixed critical vulnerability found in Cosmos DB allowed any user to remotely take over other users' databases by giving them full admin access without requiring authorization. "Microsoft has recently become aware of a vulnerability in Azure Cosmos DB that could potentially allow a user to gain access to another customer's resources by using the account's primary read-write key," the company told customers.
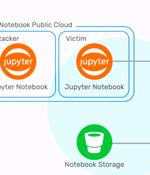
Cloud infrastructure security company Wiz on Thursday revealed details of a now-fixed Azure Cosmos database vulnerability that could have been potentially exploited to grant any Azure user full admin access to other customers' database instances without any authorization. Cosmos DB is Microsoft's proprietary NoSQL database that's advertised as "a fully managed service" that "Takes database administration off your hands with automatic management, updates and patching."
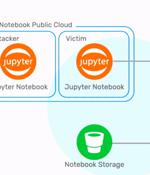
Cloud infrastructure security company Wiz on Thursday revealed details of a now-fixed Azure Cosmos database vulnerability that could have been potentially exploited to grant any Azure user full admin access to other customers' database instances without any authorization. Cosmos DB is Microsoft's proprietary NoSQL database that's advertised as "a fully managed service" that "Takes database administration off your hands with automatic management, updates and patching."

Enterprise security and network appliance vendor F5 has released patches for more than two dozen security vulnerabilities affecting multiple versions of BIG-IP and BIG-IQ devices that could potentially allow an attacker to perform a wide range of malicious actions, including accessing arbitrary files, escalating privileges, and executing JavaScript code. Chief among them is CVE-2021-23031, a vulnerability affecting BIG-IP Advanced Web Application Firewall and BIG-IP Application Security Manager that allows an authenticated user to perform a privilege escalation.

Enterprise security and network appliance vendor F5 has released patches for more than two dozen security vulnerabilities affecting multiple versions of BIG-IP and BIG-IQ devices that could potentially allow an attacker to perform a wide range of malicious actions, including accessing arbitrary files, escalating privileges, and executing JavaScript code. Chief among them is CVE-2021-23031, a vulnerability affecting BIG-IP Advanced Web Application Firewall and BIG-IP Application Security Manager that allows an authenticated user to perform a privilege escalation.