Security News > 2022 > April

Taiwanese hardware vendor QNAP urged customers on Monday to disable Universal Plug and Play port forwarding on their routers to prevent exposing their network-attached storage devices to attacks from the Internet. UPnP Port Forwarding allows network devices to communicate seamlessly and create groups for easier data sharing.
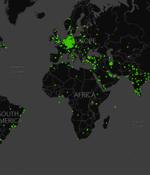
Microsoft and a consortium of cybersecurity companies took legal and technical steps to disrupt the ZLoader botnet, seizing control of 65 domains that were used to control and communicate with the infected hosts. "ZLoader is made up of computing devices in businesses, hospitals, schools, and homes around the world and is run by a global internet-based organized crime gang operating malware as a service that is designed to steal and extort money," Amy Hogan-Burney, general manager of Microsoft's Digital Crimes Unit, said.
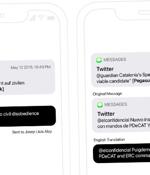
A previously unknown zero-click exploit in Apple's iMessage was used to install mercenary spyware from NSO Group and Candiru against at least 65 individuals as part of a "Multi-year clandestine operation." The attacks involved the weaponization of an iOS exploit dubbed HOMAGE that made it possible to penetrate the devices running versions prior to iOS 13.2, which was released on October 28, 2019.

Three high-impact Unified Extensible Firmware Interface security vulnerabilities have been discovered impacting various Lenovo consumer laptop models, enabling malicious actors to deploy and execute firmware implants on the affected devices. Tracked as CVE-2021-3970, CVE-2021-3971, and CVE-2021-3972, the latter two "Affect firmware drivers originally meant to be used only during the manufacturing process of Lenovo consumer notebooks," ESET researcher Martin Smolár said in a report published today.

Microsoft announced today that the 30-year-old SMBv1 file-sharing protocol is now disabled by default on Windows systems running the latest Windows 11 Home Dev channel builds, the last editions of Windows or Windows Server that still came with SMBv1 enabled. Redmond first announced plans to disable SMBv1 in most versions of the Windows operating system in June 2017 after first disabling it for internal builds of Windows 10 Enterprise and Windows Server 2016.

Tech teams worry about protecting intellectual property in addition to managing costs and ensuring reliability when selecting a cloud service provider, according to a new report. It's not an either/or situation with 20% of companies that use a smaller cloud provider also use a hyperscaler.

A new wave of cryptocurrency systems dubbed De-Fi, short for decentralised finance, has arisen to fill that transactional void. Instead of depositing your funds with a licensed and regulated bank, and then trading with those funds by choosing from a carefully curated list of transaction types, De-Fi systems let you invest your money with them, in return for access to a "Smart contract" system that allows you trade automatically with other users of the system in a way to suit yourself.

Columbia University researchers have developed a novel algorithm that can block rogue audio eavesdropping via microphones in smartphones, voice assistants, and connected devices in general. As real-world tests showed, the system can make speech impossible to discern by automatic speech recognition technology, no matter what software is used and the microphone's position.

In a September 2021 report from the nonprofit Cloud Security Alliance, nearly 70 percent of respondents - comprising 1,090 IT and security professionals - reported that their company's cloud security, IT operations and developer teams are misaligned on security policies and/or enforcement strategies. March 2021: The arts-and-crafts retailer Hobby Lobby left 138GB of sensitive customer information, source code for the company's app, and employee names and email addresses open to the public internet because of a cloud misconfiguration in its Amazon Web Services cloud database.

GitHub says it notified all organizations believed to have had data stolen from their private repositories by attackers abusing compromised OAuth user tokens issued to Heroku and Travis-CI. "As of 9:30 PM UTC on April 18, 2022, we've notified victims of this campaign whom we have identified as having repository contents downloaded by an unauthorized party through abuse of third-party OAuth user tokens maintained by Heroku and Travis CI," the company revealed in an update to the original statement. "We do not believe the attacker obtained these tokens via a compromise of GitHub or its systems, because the tokens in question are not stored by GitHub in their original, usable formats which could be abused by an attacker," GitHub said.