Security News

This is not the first time that AhMyth-based Android malware has been available on the official store; ESET previously published research on such a trojanized app in 2019. The iRecorder app can also be found on alternative and unofficial Android markets, and the developer also provides other applications on Google Play, but they don't contain malicious code.
The infamous Lazarus Group actor has been targeting vulnerable versions of Microsoft Internet Information Services servers as an initial breach route to deploy malware on targeted systems. The findings come from the AhnLab Security Emergency response Center, which detailed the advanced persistent threat's continued abuse of DLL side-loading techniques to deploy malware.

Public source code repositories, from Sourceforge to GitHub, from the Linux Kernel Archives to ReactOS.org, from PHP Packagist to the Python Package Index, better known as PyPI, are a fantastic source of free operating systems, applications, programming libraries, and developers' toolkits that have done computer science and software engineering a world of good. In cases like that, you can save time by searching for a package that already exists in one of the many available repositories, and hooking that external package into your own tree of source code.

ESET malware researchers found a new remote access trojan on the Google Play Store, hidden in an Android screen recording app with tens of thousands of installs. While first added to the store in September 2021, the 'iRecorder - Screen Recorder' app was likely trojanized via a malicious update released almost a year later, in August 2022.

The North Korean advanced persistent threat group known as Kimsuky has been observed using a piece of custom malware called RandomQuery as part of a reconnaissance and information exfiltration operation. "Lately, Kimsuky has been consistently distributing custom malware as part of reconnaissance campaigns to enable subsequent attacks," SentinelOne researchers Aleksandar Milenkoski and Tom Hegel said in a report published today.
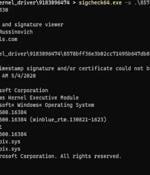
An unknown threat actor has been observed leveraging a malicious Windows kernel driver in attacks likely targeting the Middle East since at least May 2020. A key security measure to mitigate against malicious drivers is Driver Signature Enforcement, which ensures that only drivers signed by Microsoft can be loaded on the system.

To address this issue and provide practical prevention solutions, Criminal IP, a CTI search engine developed by AI SPERA, launched a comprehensive Chrome extension named "Criminal IP Phishing scams link checker" on May 22, 2023. A web browsing guard against Phishing, Malware, and Ransomware based on AI. This Criminal IP's Chrome extension offers real-time scanning of websites worldwide, using AI-based detection to identify recently created phishing sites.

PyPI, the official third-party registry of open source Python packages has temporarily suspended new users from signing up, and new projects from being uploaded to the platform until further notice. As of today, the Python Package Index, more commonly known as PyPI, has temporarily suspended new user registrations and project creations until further notice.

A new malware distribution campaign is underway impersonating the CapCut video editing tool to push various malware strains to unsuspecting victims. Threat actors exploit this by creating websites that distribute malware disguised as CapCut installers.

Researchers have discovered multiple npm packages named after NodeJS libraries that even pack a Windows executable that resembles NodeJS but instead drops a sinister trojan. These packages, given their stealthiness and a very low detection rate, had been present on npm for over two months prior to their detection by the researchers.