Security News
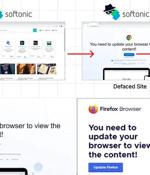
Threat actors have been observed serving malicious code by utilizing Binance's Smart Chain (BSC) contracts in what has been described as the "next level of bulletproof hosting." The campaign,...

This is to deal with a recent outbreak of malicious updates pushing malware from compromised publisher accounts. Starting in late August and into September 2023, there has been an elevated number of reports about compromised Steamworks accounts and the attackers uploading malicious builds that infect players with malware.

A new, lightweight variant of the RomCom backdoor was deployed against participants of the Women Political Leaders Summit in Brussels, a summit focusing on gender equality and women in politics. Designed to imitate the real Women Political Leaders website hosted on wplsummit.org.

Between July and September, DarkGate malware attacks have used compromised Skype accounts to infect targets through messages containing VBA loader script attachments. According to Trend Micro security researchers who spotted the attacks, this script downloads a second-stage AutoIT script designed to drop and execute the final DarkGate malware payload. "Access to the victim's Skype account allowed the actor to hijack an existing messaging thread and craft the naming convention of the files to relate to the context of the chat history," Trend Micro said.
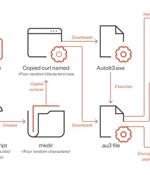
A piece of malware known as DarkGate has been observed being spread via instant messaging platforms such as Skype and Microsoft Teams. In these attacks, the messaging apps are used to deliver a...

A newly discovered campaign dubbed "Stayin' Alive" has been targeting government organizations and telecommunication service providers across Asia since 2021, using a wide variety of "Disposable" malware to evade detection. The attacks appear to originate from the Chinese espionage actor known as 'ToddyCat,' which relies on spear-phishing messages carrying malicious attachments to load a variety of malware loaders and backdoors.
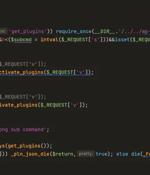
Cybersecurity researchers have shed light on a new sophisticated strain of malware that masquerades a WordPress plugin to stealthily create administrator accounts and remotely control a...

In Q2 2023, 95% of malware now arrives over encrypted connections, endpoint malware volumes are decreasing despite campaigns growing more widespread, ransomware detections are declining amid a rise in double-extortion attacks, and older software vulnerabilities persist as popular targets for exploitation among modern threat actors, among other trends, according to WatchGuard. "The data analyzed by our Threat Lab for our latest report reinforces how advanced malware attacks fluctuate in occurrence and multifaceted cyber threats continue to evolve, requiring constant vigilance and a layered security approach to combat them effectively," said Corey Nachreiner, CSO at WatchGuard.

A Mirai-based DDoS malware botnet tracked as IZ1H9 has added thirteen new payloads to target Linux-based routers and routers from D-Link, Zyxel, TP-Link, TOTOLINK, and others. IZ1H9 compromises devices to enlist them to its DDoS swarm and then launches DDoS attacks on specified targets, presumably on the order of clients renting its firepower.

Microsoft is planning to phase out VBScript in future Windows releases after 30 years of use, making it an on-demand feature until it is removed. With the July 2019 Patch Tuesday cumulative updates, Microsoft also disabled VBScript by default in Internet Explorer 11 on Windows 10.