Security News

The Unified Extensible Firmware Interface (UEFI) code from various independent firmware/BIOS vendors (IBVs) has been found vulnerable to potential attacks through high-impact flaws in image...

Cybercriminals are targeting Mac users with a new proxy trojan malware bundled with popular, copyrighted macOS software being offered on warez sites. Proxy trojan malware infects computers, turning them into traffic-forwarding terminals used to anonymize malicious or illegal activities such as hacking, phishing, and transactions for illicit goods.

A Russian national has been found guilty in connection with his role in developing and deploying a malware known as TrickBot, the U.S. Department of Justice (DoJ) announced. Vladimir Dunaev, 40,...

On Thursday, a Russian national pleaded guilty to charges related to his involvement in developing and deploying the Trickbot malware, which was used in attacks against hospitals, companies, and individuals in the United States and worldwide. According to court documents, a 40-year-old individual, also known as FFX, oversaw the development of TrickBot's browser injection component as a malware developer.

A novel malware named 'Agent Raccoon' is being used in cyberattacks against organizations in the United States, the Middle East, and Africa. Agent Raccoon is a.NET malware disguised as a Google Update or Microsoft OneDrive Updater that leverages the DNS protocol to establish a covert communication channel with the attackers' C2 infrastructure.
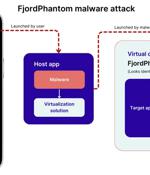
Cybersecurity researchers have disclosed a new sophisticated Android malware called FjordPhantom that has been observed targeting users in Southeast Asian countries like Indonesia, Thailand, and...

A new Android malware named FjordPhantom has been discovered using virtualization to run malicious code in a container and evade detection. The malware was discovered by Promon, whose analysts report that it currently spreads via emails, SMS, and messaging apps targeting banking apps in Indonesia, Thailand, Vietnam, Singapore, and Malaysia.

"Malware free" attacks, attackers' increased reliance on legitimate tools and scripting frameworks, and BEC scams were the most prominent threats small and medium businesses faced in Q3 2023, says the inaugural SMB Threat Report by Huntress, a company that provides a security platform and services to SMBs and managed service providers. Attackers deployed malware in 44% of cases, but the remaining 56% of incidents included use of "Living off the land" binaries, scripting frameworks and remote monitoring and management software.

The North Korean threat actors behind macOS malware strains such as RustBucket and KANDYKORN have been observed "mixing and matching" different elements of the two disparate attack chains,...

The 'ClearFake' fake browser update campaign has expanded to macOS, targeting Apple computers with Atomic Stealer malware. The ClearFake campaign started in July this year to target Windows users with fake Chrome update prompts that appear on breached sites via JavaScript injections.