Security News
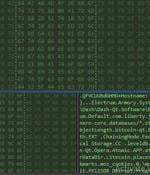
A new malware campaign has been observed targeting Italy with phishing emails designed to deploy an information stealer on compromised Windows systems. "The info-stealer malware steals sensitive information like system info, crypto wallet and browser histories, cookies, and credentials of crypto wallets from victim machines," Uptycs security researcher Karthickkumar Kathiresan said in a report.

Within a few weeks of ChatGPT going live, participants in cybercrime forums-some with little or no coding experience-were using it to write software and emails that could be used for espionage, ransomware, malicious spam, and other malicious tasks.The Python code combined various cryptographic functions, including code signing, encryption, and decryption.

The Kinsing malware is now actively breaching Kubernetes clusters by leveraging known weaknesses in container images and misconfigured, exposed PostgreSQL containers. "Recently, we identified a widespread campaign of Kinsing that targeted vulnerable versions of WebLogic servers," reads a report by Microsoft security researcher Sunders Bruskin.

The threat actors behind the Kinsing cryptojacking operation have been spotted exploiting misconfigured and exposed PostgreSQL servers to obtain initial access to Kubernetes environments. Kinsing has a storied history of targeting containerized environments, often leveraging misconfigured open Docker daemon API ports as well as abusing newly disclosed exploits to drop cryptocurrency mining software.

The Russian cyberespionage group known as Turla has been observed piggybacking on attack infrastructure used by a decade-old malware to deliver its own reconnaissance and backdoor tools to targets in Ukraine. Google-owned Mandiant, which is tracking the operation under the uncategorized cluster moniker UNC4210, said the hijacked servers correspond to a variant of a commodity malware called ANDROMEDA that was uploaded to VirusTotal in 2013.

A variant of the bad penny that is Dridex, the general-purpose malware that has been around for years, now has macOS platforms in its sights and a new way of delivering malicious macros via documents. While the Dridex variant has macOS systems in its sights, the malicious payload it delivers is a Microsoft exe file, which won't run in a MacOS environment.
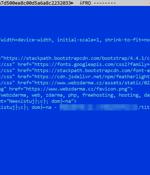
A variant of the infamous Dridex banking malware has set its sights on Apple's macOS operating system using a previously undocumented infection method, according to latest research. Previous Dridex campaigns targeting Windows have leveraged macro-enabled Microsoft Excel documents sent via phishing emails to deploy the payload. A law enforcement operation orchestrated by Europe and the U.S. disrupted the botnet in October 2015 and a Moldovan national named Andrey Ghinkul was arrested for his role as an administrator of the operation.

The Android malware family tracked as SpyNote has had a sudden increase in detections in the final quarter of 2022, which is attributed to a source code leak of one of its latest, known as 'CypherRat. Threat actors quickly snatched the malware's source code and launched their own campaigns.

A new Linux malware downloader created using SHC has been spotted in the wild, infecting systems with Monero cryptocurrency miners and DDoS IRC bots. According to ASEC researchers, who discovered the attack, the SHC loader was uploaded to VirusTotal by Korean users, with attacks generally focused on Linux systems in the same country.

Hackers are abusing the Windows Problem Reporting error reporting tool for Windows to load malware into a compromised system's memory using a DLL sideloading technique. The use of this Windows executable is to stealthy infect devices without raising any alarms on the breached system by launching the malware through a legitimate Windows executable.