Security News

Malware targeting Linux systems increased by 35% in 2021 compared to 2020. XorDDoS, Mirai and Mozi malware families accounted for over 22% of Linux-targeted threats observed by CrowdStrike in 2021.

Researchers have disclosed details of two critical security vulnerabilities in Control Web Panel that could be abused as part of an exploit chain to achieve pre-authenticated remote code execution on affected servers. Tracked as CVE-2021-45467, the issue concerns a case of a file inclusion vulnerability, which occurs when a web application is tricked into exposing or running arbitrary files on the web server.

The number of malware infections targeting Linux devices rose by 35% in 2021, most commonly to recruit IoT devices for DDoS attacks. In 2021, there was a 35% rise in malware targeting Linux systems compared to 2020.

With FDE, everything gets encrypted, including unused parts of the disk, deleted sectors, filenames, swapfile data, the apps you're using, the operating system files you've installed, and even the disk space you've deliberately zeroed out to forcibly overwrite what was there before. Did you use the right cryptographic algorithm? Did you generate the encryption keys reliably? Did you handle the issue of data integrity properly? Can you change passwords safely and quickly? How easy is it to lock yourself out by mistake? What if you want to adjust the encryption parameters as your corporate policies evolve?
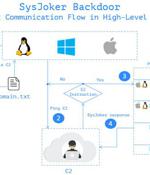
A new cross-platform backdoor called "SysJoker" has been observed targeting machines running Windows, Linux, and macOS operating systems as part of an ongoing espionage campaign that's believed to have been initiated during the second half of 2021. "SysJoker masquerades as a system update and generates its by decoding a string retrieved from a text file hosted on Google Drive," Intezer researchers Avigayil Mechtinger, Ryan Robinson, and Nicole Fishbein noted in a technical write-up publicizing their findings.

A new multi-platform backdoor malware named 'SysJoker' has emerged in the wild, targeting Windows, Linux, and macOS with the ability to evade detection on all three operating systems. The discovery of the new malware comes from researchers at Intezer who first saw signs of its activity in December 2021 after investigating an attack on a Linux-based web server.

A new multi-platform backdoor malware named 'SysJocker' has emerged in the wild, targeting Windows, Linux, and macOS with the ability to evade detection on all three operating systems. The discovery of the new malware comes from researchers at Intezer who first saw signs of its activity in December 2021 after investigating an attack on a Linux-based web server.

Dubbed SysJoker by Intezer, the backdoor is used for establishing initial access on a target machine. A possible attack vector for SysJoker is an infected npm package, according to Intezer's analysis - an increasingly popular vector for dropping malware on targets.

AvosLocker is the latest ransomware gang that has added support for encrypting Linux systems to its recent malware variants, specifically targeting VMware ESXi virtual machines. While we couldn't find what targets were targeted using this AvosLocker ransomware Linux variant, BleepingComputer knows of at least one victim that got hit with a $1 million ransom demand.

Linux Mint has released version 20.3, codenamed 'Una,' as a long-term support version that will receive security updates until 2025. Long-term support releases are for those who favor stability over bleeding-edge software and experimental features, so Linux Mint 20.3 is ideal for those who want to keep the same system without significant changes for years.