Security News

The latest revelation from law enforcement authorities in relation to this week's LockBit leaks is that the ransomware group had registered nearly 200 "Affiliates" over the past two years. List of LockBit 3.0 affiliates published by the NCA. The FBI first started investigating LockBit in 2020, and the group has since developed new variants of its ransomware, the latest of which was released in mid-2022, so the data shared today likely shows all the affiliates that have ever deployed the most recent version of LockBit.

The alleged source code for the third iteration of the Knight ransomware is being offered for sale to a single buyer on a hacker forum by a representative of the operation. Knight ransomware launched at the end of July 2023 as a re-brand of the Cyclops operation, targeting Windows, macOS, and Linux/ESXi systems.

Indian tech services giant Infosys has been named as the source of a data leak suffered by the Bank of America. Infosys disclosed the breach in a November 3, 2023, filing [PDF] that revealed its US subsidiary Infosys McCamish Systems LLC "Has become aware of a cyber security incident resulting in non-availability of certain applications and systems in IMS.".
A now-patched security flaw in Microsoft Outlook could be exploited by threat actors to access NT LAN Manager (NTLM) v2 hashed passwords when opening a specially crafted file. The issue, tracked...

A new vulnerability dubbed 'LeftoverLocals' affecting graphics processing units from AMD, Apple, Qualcomm, and Imagination Technologies allows retrieving data from the local memory space. [...]
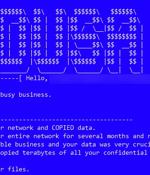
The threat actors associated with the Medusa ransomware have ramped up their activities following the debut of a dedicated data leak site on the dark web in February 2023 to publish sensitive data...

Popular athleisure clothing brand Halara is investigating a data breach after the alleged data of almost 950,000 customers was leaked on a hacking forum. Halara told BleepingComputer that it is aware that customer data was allegedly stolen and leaked online and is investigating a potential breach.

The LockBit ransomware operation has claimed responsibility for a November 2023 cyberattack on the Capital Health hospital network and threatens to leak stolen data and negotiation chats by tomorrow. The LockBit ransomware gang has now claimed responsibility for the attack on Capital Health by listing the healthcare company on its data leak extortion portal yesterday.

The U.S. division of Xerox Business Solutions has been compromised by hackers with a limited amount of personal information possibly exposed, according to a statement by the parent company, Xerox Corporation. INC Ransom ransomware gang added the corporation to its extortion portal on December 29, claiming to have stolen sensitive data and confidential documents from its systems.

Cybercrime actor DragonForce which claimed responsibility for the attack has also leaked 95 GB of data that it states, belongs to the company. In a statement to BleepingComputer, Yakult Australia confirmed it was investigating a cyber incident that occurred in mid-December.