Security News

The San Francisco 49ers were recently kneecapped by a BlackByte ransomware attack that temporarily discombobulated the NFL team's corporate IT network on the Big Buffalo Wing-Snarfing Day itself: Superbowl Sunday. Joseph Carson, chief security scientist and advisory CISO at provider of privileged access management solutions provider Delinea, suggested to Threatpost that it's likely that an affiliate hacked the 49ers, as opposed to the authors behind the ransomware, given that BlackByte is an RaaS. BlackByte recently posted some files purportedly stolen from the team on a dark web site in a file marked "2020 Invoices." The gang hasn't made its ransom demands public.

The US Federal Bureau of Investigation revealed that the BlackByte ransomware group has breached the networks of at least three organizations from US critical infrastructure sectors in the last three months. "As of November 2021, BlackByte ransomware had compromised multiple US and foreign businesses, including entities in at least three US critical infrastructure sectors.," the federal law enforcement agency said [PDF].

80% of critical infrastructure organizations experienced a ransomware attack in the last year, with an equal number reporting that their security budgets have risen since 2020, a Claroty report reveals. The report is based on an independent global survey of 1,100 information technology and operational technology professionals who work in critical infrastructure sectors, exploring how they have dealt with the significant challenges in 2021, their levels of resiliency, and priorities moving forward.

Ransomware attacks are proliferating as criminals turn to gangs providing turnkey post-compromise services, Britain's National Cyber Security Centre has warned. The warning comes hot on the heels of several high-profile attacks against oil distribution companies and also businesses that operate ports in the West - though today's note insists there was a move by criminals away from "Big game hunting" against US targets.

Critical infrastructure suffered ransomware attacks, with threat actors targeting an oil petrol distributor and oil terminals in major ports in different attacks. Oil terminals in major ports disclosed that they too suffered ransomware attacks.

Investments in non-cloud infrastructure increased 7.3% year over year in 3Q21 to $14.6 billion, the third consecutive quarter to see an increase in year-over-year spend after a period of declining spending that started in 2Q19. Spending on shared cloud infrastructure reached $13 billion, an increase of 8.6% compared to 3Q20, and a 6.6% increase from the previous quarter. IDC expects to see continuously strong demand for shared cloud infrastructure with spending surpassing non-cloud infrastructure spending in 2022.
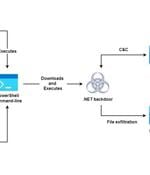
An active espionage campaign has been attributed to the threat actor known as Molerats that abuses legitimate cloud services like Google Drive and Dropbox to host malware payloads and for command-and-control and the exfiltration of data from targets across the Middle East. The cyber offensive is believed to have been underway since at least July 2021, according to cloud-based information security company Zscaler, continuing previous efforts by the hacking group to conduct reconnaissance on the target hosts and plunder sensitive information.

NIS is the main law controlling security practices in the UK today. Currently a straight copy of the EU NIS Directive, one of the benefits of Brexit leapt upon by the Department for Digital, Culture, Media and Sport is the new ability to amend NIS's reporting thresholds.

The coordinated cyberattacks targeting Ukrainian government websites and the deployment of a data-wiper malware called WhisperGate on select government systems are part of a broader wave of malicious activities aimed at sabotaging critical infrastructure in the country. "The attack used vulnerabilities in the site's content management systems and Log4j, as well as compromised accounts of employees of the development company," the SSU said, corroborating prior disclosure from the Ukraine CERT team.

Some 15 server infrastructures used by crims to prepare ransomware attacks were seized by cops yesterday as part of an international sting to take down VPNLab.net. The VPN provider's service gave users "Shielded communications and internet access" that was used in "Support of serious criminals acts such as ransomware deployment and other cybercrime activities," Europol said today.