Security News

GitHub announced today the introduction of passwordless authentication support in public beta, allowing users to upgrade from security keys to passkeys. To activate passkeys on your account, click your profile photo in the top-right corner of any GitHub page.

Millions of GitHub repositories may be vulnerable to dependency repository hijacking, also known as "RepoJacking," which could help attackers deploy supply chain attacks impacting a large number of users. The warning comes from AquaSec's security team, 'Nautilus,' who analyzed a sample of 1.25 million GitHub repositories and found that about 2.95% of them to be vulnerable to RepoJacking.

Millions of software repositories on GitHub are likely vulnerable to an attack called RepoJacking, a new study has revealed. Aqua said a threat actor could leverage websites like GHTorrent to extract GitHub metadata associated with any public commits and pull requests to compile a list of unique repositories.

At least half of dozen GitHub accounts from fake researchers associated with a fraudulent cybersecurity company have been observed pushing malicious repositories on the code hosting service. VulnCheck, which discovered the activity, said, "The individuals creating these repositories have put significant effort into making them look legitimate by creating a network of accounts and Twitter profiles, pretending to be part of a non-existent company called High Sierra Cyber Security."

Hackers are impersonating cybersecurity researchers on Twitter and GitHub to publish fake proof-of-concept exploits for zero-day vulnerabilities that infect Windows and Linux with malware. These malicious exploits are promoted by alleged researchers at a fake cybersecurity company named 'High Sierra Cyber Security,' who promote the GitHub repositories on Twitter, likely to target cybersecurity researchers and firms involved in vulnerability research.

Open-source GitHub cybersecurity projects, developed and maintained by dedicated contributors, provide valuable tools, frameworks, and resources to enhance security practices. Faraday is used through the terminal and allows users to take advantage of community tools in a multiuser environment.
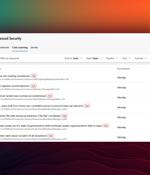
GitHub has announced that its application security testing tools are now more widely available for subscribers of Microsoft's Azure DevOps Services. "GitHub Advanced Security for Azure DevOps can not only help you find secrets that have already been exposed in Azure Repos, but also help you prevent new exposures by blocking any pushes to Azure Repos that contain secrets," says Aaron Hallberg, Director of Product for Azure DevOps, Microsoft.

GitHub's Chief Security Officer and SVP of Engineering shared more details today on a string of outages that hit the code hosting platform last week. The second outage, occurring on May 10, impacted the issuance of authentication tokens for GitHub Apps and resulted from high load and inefficient implementation of an API responsible for managing GitHub App permissions.
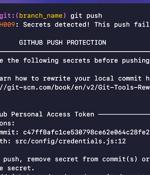
GitHub has announced the general availability of a new security feature called push protection, which aims to prevent developers from inadvertently leaking keys and other secrets in their code. The Microsoft-owned cloud-based repository hosting platform, which began testing the feature a year ago, said it's also extending push protection to all public repositories at no extra cost.

GitHub is making push protection - a security feature designed to automatically prevent the leaking of secrets to repositories - free for owners of all public repositories. Prevent leaking secrets with GitHub push protection.