Security News
A password-less database containing an estimated 1.3 million sets of Dutch COVID-19 testing records was left exposed to the open internet, and it's not clear if anyone is taking responsibility.Among the information revealed in the publicly accessible and seemingly insecurely configured database were 118,441 coronavirus test certificates, 506,663 appointment records, 660,173 testing samples and "a small number" of internal files.
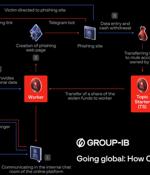
The Classiscam scam-as-a-service program has reaped the criminal actors $64.5 million in illicit earnings since its emergence in 2019. Germany, Poland, Spain, Italy, and Romania accounted for the highest number of fraudulent transactions registered in Classiscam chats.

Credential phishing attacks continue to exploit COVID-19 to target businesses. Since early 2020, the coronavirus pandemic has given cyber criminals another area that's ripe for exploitation as they try to trick individuals and businesses into divulging sensitive information.

In the latest attacks, phishing emails impersonate the U.S. Small Business Administration and abuse Google Forms to host phishing pages that steal the personal details of business owners. The lures used in the phishing emails are for pandemic financial support programs like the "Paycheck Protection Program", "Revitalization Fund", and "COVID Economic Injury Disaster Loan.".

Resecurity, a California-based cybersecurity company protecting Fortune 500, has identified leaked PII stolen from Thailand's Department of Medical Sciences containing information about citizens with COVID-19 symptoms. The incident was uncovered and shared with Thai CERT. The data was put for sale on several Dark Web marketplaces and was available for further purchase via a Telegram channel created by the bad actors.

Quick show of hands: who came home from this year's RSA Conference without COVID-19? RSA Conference organizers required all attendees to show proof of vaccination or a negative test for their first entry into Moscone Center.

WithSecure and Cue Health have worked together to address a security issue that WithSecure discovered in Cue's COVID-19 test, which delivers the results of a nasal swab test via bluetooth to a mobile device. The COVID-19 test is a molecular test that offers users results in 20 minutes with accuracy that's comparable to PCR tests performed in labs.

A China-based threat group is likely running a month-long campaign using a variant of the Korplug malware and targeting European diplomats, internet service providers and research institutions via phishing lures that refer to Russia's invasion of Ukraine and COVID-19 travel restrictions. The ongoing campaign was first seen in August 2021 and is being tied to Mustang Panda - a Chinese APT unit also known as TA416, RedDelta and PKPLUG - due to similar code and common tactics, techniques and procedures used by the group in the past, according to researchers with the cybersecurity firm ESET. Mustang Panda is known for targeting governmental entities and non-governmental organizations, with most of its victims being in East and Southeast Asia.

How COVID-19 vaccine passport apps fail to secure data. In addition to failing to protect the data encoded by the QR code, 27 of the 40 vaccine passport apps that Symantec tested turned out to have risky behavior typically associated with mobile apps.

The Russia-linked threat actor known as APT29 targeted European diplomatic missions and Ministries of Foreign Affairs as part of a series of spear-phishing campaigns mounted in October and November 2021. The spear-phishing attacks commenced with a COVID-19-themed phishing email impersonating the Iranian Ministry of Foreign Affairs and containing an HTML attachment that, when opened, prompts the recipients to open or save what appears to be an ISO disk image file.