Security News

Zeppelin ransomware is back and employing new compromise and encryption tactics in its recent campaigns against various vertical industries-particularly healthcare-as well as critical infrastructure organizations, the feds are warning. Zeppelin also appears to have a new multi-encryption tactics, executing the malware more than once within a victim's network and creating different IDs and file extensions for multiple instances attack, according to the CISA. "This results in the victim needing several unique decryption keys," according to the advisory.
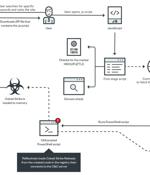
The operators of the Gootkit access-as-a-service malware have resurfaced with updated techniques to compromise unsuspecting victims. "In the past, Gootkit used freeware installers to mask malicious files; now it uses legal documents to trick users into downloading these files," Trend Micro researchers Buddy Tancio and Jed Valderama said in a write-up last week.

Researchers have disclosed details about a security vulnerability in the Netwrix Auditor application that, if successfully exploited, could lead to arbitrary code execution on affected devices. "Since this service is typically executed with extensive privileges in an Active Directory environment, the attacker would likely be able to compromise the Active Directory domain," Bishop Fox said in an advisory published this week.

Black Lotus Labs, a threat intelligence team within Lumen Technologies, has recently exposed a new modus operandi for an attack campaign that went undiscovered for nearly two years. One of its most intriguing characteristics is that it targets small office / home office routers as an initial point of compromise, in addition to being particularly stealth.

Generically, the industry has conformed to the term Business Email Compromise to capture this swath of threats, including impersonation, phishing, spoofing, and in more advanced cases, by way of a malicious attachment, including Adobe and Microsoft Office documents. To help address this gap, we launched InQuest Labs, a free research portal designed to crowdsource the discovery of emerging threats.

Since 2020, Chinese state-sponsored threat actors have operated large attack campaigns exploiting publicly identified security vulnerabilities. In these campaigns, the attackers receive valid account access by exploiting Virtual Private Network vulnerabilities or other Internet-facing services without using their own distinctive or identifying malware, making it harder for threat intelligence analysts to evaluate the threat.

FBI: $43 billion in losses are due to Business Email Compromise fraud between 2016 and 2021. The Federal Bureau of Investigation released an alert that said there has been a 65% increase in identified global exposed losses from Business Email Compromise fraud, also known as Email Account Compromise.

The Federal Bureau of Investigation said today that the amount of money lost to business email compromise scams continues to grow each year, with a 65% increase in the identified global exposed losses between July 2019 and December 2021. Victims reported losses of almost $2.4 billion in 2021, based on 19,954 recorded complaints linked to BEC attacks targeting individuals and businesses.

Security analysts have uncovered a recent phishing campaign from Russian hackers known as APT29 targeting diplomats and government entities. In a new campaign spotted by threat analysts at Mandiant, APT29 is targeting diplomats and various government agencies through multiple phishing campaigns.

A server-side request forgery flaw in an API of a large financial technology platform potentially could have compromised millions of bank customers, allowing attackers to defraud clients by controlling their bank accounts and funds, researchers have found. A team at Salt Security's Salt Labs identified the vulnerability in an API in a web page that supports the organization's platform fund transfer functionality, which allows clients to transfer money from their accounts on its platform into their bank accounts, researchers disclosed in a report published Thursday.