Security News

A critical vulnerability in the F5 BIG-IP configuration utility, tracked as CVE-2023-46747, allows an attacker with remote access to the configuration utility to perform unauthenticated remote code execution."This vulnerability may allow an unauthenticated attacker with network access to the BIG-IP system through the management port and/or self IP addresses to execute arbitrary system commands," reads F5's security bulletin.

F5 has alerted customers of a critical security vulnerability impacting BIG-IP that could result in unauthenticated remote code execution. The issue, rooted in the configuration utility component,...

VMware issued security updates to fix a critical vCenter Server vulnerability that can be exploited to gain remote code execution attacks on vulnerable servers. vCenter Server is the central management hub for VMware's vSphere suite, and it helps administrators manage and monitor virtualized infrastructure.

The TorchServe flaws discovered by the Oligo Security research team can lead to unauthorized server access and remote code execution on vulnerable instances. Due to insecure deserialization in the SnakeYAML library, attackers can upload a model with a malicious YAML file to trigger remote code execution.

Cybersecurity researchers have disclosed multiple critical security flaws in the TorchServe tool for serving and scaling PyTorch models that could be chained to achieve remote code execution on...
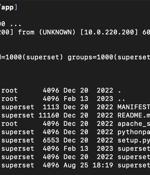
Patches have been released to address two new security vulnerabilities in Apache SuperSet that could be exploited by an attacker to gain remote code execution on affected systems. Outside of these weaknesses, the latest version of Superset also remediates a separate improper REST API permission issue that allows for low-privilege users to carry out server-side request forgery attacks.

Three critical-severity remote code execution vulnerabilities impact ASUS RT-AX55, RT-AX56U V2, and RT-AC86U routers, potentially allowing threat actors to hijack devices if security updates are not installed.The flaws, which all have a CVSS v3.1 score of 9.8 out of 10.0, are format string vulnerabilities that can be exploited remotely and without authentication, potentially allowing remote code execution, service interruptions, and performing arbitrary operations on the device.

WinRAR could start a wrong file after a user double- clicked an item in a specially crafted archive. That's a bit like receiving an email containing a safe-looking attachment along with a risky-looking one, deciding to start by investigating only the safe-looking one, but unknowingly firing up the risky file instead. From what we can tell, and in another irony, this bug existed in WinRAR's code for unpacking ZIP files, not in the code for processing its very own RAR file format.

A widely used Windows-only utility, WinRAR can create and extract file archives in various compression formats. CVE-2023-40477 is a remote code execution vulnerability that could allow remote threat actors to execute arbitrary code on an affected WinRAR installation.
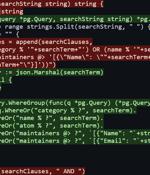
Multiple SQL injection vulnerabilities have been disclosed in Gentoo Soko that could lead to remote code execution on vulnerable systems. "These SQL injections happened despite the use of an Object-Relational Mapping library and prepared statements," SonarSource researcher Thomas Chauchefoin said, adding they could result in RCE on Soko because of a "Misconfiguration of the database."