Security News

A large-scale campaign involving over 800 compromised WordPress websites is spreading banking trojans that target the credentials of Brazilian e-banking users. Although the security firm notified the Brazilian CERT, the campaign is ongoing, with hundreds of websites still compromised with malicious scripts that push the malware.
Google Chrome has announced plans to prohibit public websites from directly accessing endpoints located within private networks as part of an upcoming major security shakeup to prevent intrusions via the browser. The proposed change is set to be rolled out in two phases as part of releases Chrome 98 and Chrome 101 scheduled in the coming months via a newly implemented W3C specification called private network access.

Google has rolled out the first round of updates to its Chrome web browser for 2022 to fix 37 security issues, one of which is rated Critical in severity and could be exploited to pass arbitrary code and gain control over a victim's system. Security researcher Yangkang of Qihoo 360 ATA, who has previously disclosed zero-day vulnerabilities in Apple's WebKit, has been credited with discovering and reporting the flaw on November 30, 2021.

Google says Manifest V3 is focused on security, privacy and performance, but it could also break Chrome browser extensions used by millions of people. The EFF is right, and Google's plans for MV3 is yet another reason why the best browser for Linux, Windows and Mac isn't Google Chrome.

Let's start with Microsoft, which put out a summary of its security updates here. Microsoft Defender for IoT: A critical remote-code execution flaw in this security product, prior to version 10.5.2, can be exploited over a network by a non-authenticated miscreant.

Google has released Chrome 96.0.4664.110 for Windows, Mac, and Linux, to address a high-severity zero-day vulnerability exploited in the wild. Although the company says this update may take some time to reach all users, the update has already begun rolling out Chrome 96.0.4664.110 worldwide in the Stable Desktop channel.

Google has rolled out fixes for five security vulnerabilities in its Chrome web browser, including one which it says is being exploited in the wild, making it the 17th such weakness to be disclosed since the start of the year. An anonymous researcher has been credited with discovering and reporting the flaw.
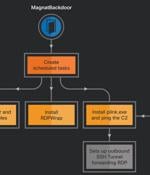
A series of malicious campaigns have been leveraging fake installers of popular apps and games such as Viber, WeChat, NoxPlayer, and Battlefield as a lure to trick users into downloading a new backdoor and an undocumented malicious Google Chrome extension with the goal of stealing credentials and data stored in the compromised systems as well as maintaining persistent remote access. A noteworthy aspect of the intrusions is the use of malvertising as a means to strike individuals who are looking for popular software on search engines to present them links to download fake installers that drop a password stealer called RedLine Stealer, a Chrome extension dubbed "MagnatExtension" that's programmed to record keystrokes and capture screenshots, and an AutoIt-based backdoor that establishes remote access to the machine.

Microsoft Edge is now displaying in-browser alerts that discourage users from downloading Google Chrome by bashing the popular browser. A few weeks later, Google began telling Microsoft Edge users to switch to Chrome to use browser extensions more securely.

Google Chrome 96 was released yesterday, and users are reporting problems with Twitter, Discord, and Instagram caused by the new version. After upgrading to Chrome 96, users report errors in their Twitter notifications, with the website warning that "Something went wrong. Try reloading," as shown below.