Security News
The prolific Iranian nation-state group known as Charming Kitten targeted multiple victims in the U.S., Europe, the Middle East and India with a novel malware dubbed BellaCiao, adding to its ever-expanding list of custom tools. Discovered by Bitdefender Labs, BellaCiao is a "Personalized dropper" that's capable of delivering other malware payloads onto a victim machine based on commands received from an actor-controlled server.

Due to the increasing importance of multi-cloud and the intricate nature of cloud infrastructure, obtaining a comprehensive understanding of the various cloud workloads operating within your system, and ensuring their security, can be challenging. In this Help Net Security video, Kaus Phaltankar, CEO at Caveonix discusses how in today's complex multi-cloud landscape, the role of CISOs is more crucial than ever.

Multi-cloud data storage, once merely a byproduct of the great cloud migration, has now become a strategy for data management. As ransomware attacks continue to rise at a 13% growth rate year over year, surely more cloud storage simply equals more data vulnerability gaps to fill, right? New developments in data technology address these concerns.

Essendant, a wholesale distributor of stationary and office supplies, is experiencing a multi-day systems "Outage" preventing customers and suppliers from placing and fulfilling online orders. Headquartered in Deerfield, Illinois, Essendant also operates in Dubai, UAE. A systems outage at Essendant is preventing the placement or fulfillment of online orders, thereby impacting both the company's customers and suppliers.

Satellite broadcast provider and TV giant Dish Network has finally confirmed that a ransomware attack was the cause of a multi-day network and service outage that started on Friday.As BleepingComputer reported, this widespread outage hit Dish.com, the Dish Anywhere app, Boost Mobile, and other websites and networks owned and operated by Dish Network.

In an email to The Register on Monday morning, a Dish spokesperson said the satellite TV company is working to restore all of its systems "As quickly as possible," but declined to answer questions about whether the outage was due to a ransomware infection, as has been widely speculated on social media. "We experienced a systems issue with our corporate network on February 23 that is affecting our internal servers and telephone systems, and the issue is being investigated," the Dish spokesperson said.

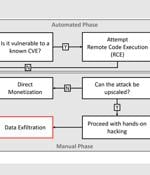
Web hosting services provider GoDaddy on Friday disclosed a multi-year security breach that enabled unknown threat actors to install malware and siphon source code related to some of its services. GoDaddy said in December 2022, it received an unspecified number of customer complaints about their websites getting sporadically redirected to malicious sites, which it later found was due to the unauthorized third party gaining access to servers hosted in its cPanel environment.

Web hosting giant GoDaddy says unknown attackers have stolen source code and installed malware on its servers after breaching its cPanel shared hosting environment. While GoDaddy discovered the security breach in early December 2022 following customer reports that their sites were being used to redirect to random domains, the attackers had access to the company's network for multiple years.

The victim will need to pay in that 20% themselves - indeed, they'd jolly well better pay in quickly, the scammers claim, given that the "Authorities" are now involved and looking for their share. Once you realise you've been scammed, whether the scammers pull the plug on you, or you pull the plug on them, you may "Co-incidentally" be contacted by someone who sympathises with your plight, and who knows just the thing for you to try next.

"Broadly speaking, digital sovereignty means having control of your digital destiny," explains Tim Phipps, director of cloud alliances at French technology group Thales. Data is what many people think of first when they hear the term digital sovereignty.