Security News
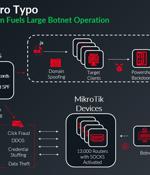
A global network of about 13,000 hijacked Mikrotik routers has been employed as a botnet to propagate malware via spam campaigns, the latest addition to a list of botnets powered by MikroTik...

A newly discovered botnet of 13,000 MikroTik devices uses a misconfiguration in domain name server records to bypass email protections and deliver malware by spoofing roughly 20,000 web domains. [...]
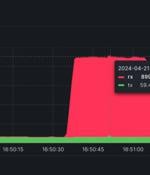
French cloud computing firm OVHcloud said it mitigated a record-breaking distributed denial-of-service (DDoS) attack in April 2024 that reached a packet rate of 840 million packets per second...

Analyzing some of those attacks revealed the extensive use of core network devices, particularly Mikrotik models, making the attacks more impactful and challenging to detect and stop. Record-breaking DDoS. Earlier this year, OVHcloud had to mitigate a massive packet rate attack that reached 840 Mpps, surpassing the previous record holder, an 809 Mpps DDoS attack targeting a European bank, which Akamai mitigated in June 2020.

Key factors for effective security automationIn this Help Net Security interview, Oliver Rochford, Chief Futurist at Tenzir, discusses how automation can be strategically integrated with human expertise, the challenges in ensuring data integrity, and the considerations when automating advanced tasks. MikroTik vulnerability could be used to hijack 900,000 routersA privilege escalation vulnerability could allow attackers to commandeer up to 900,000 MikroTik routers, says VulnCheck researcher Jacob Baines.

A privilege escalation vulnerability (CVE-2023-30799) could allow attackers to commandeer up to 900,000 MikroTik routers, says VulnCheck researcher Jacob Baines. While exploting it does require...

A severe privilege escalation issue impacting MikroTik RouterOS could be weaponized by remote malicious actors to execute arbitrary code and seize full control of vulnerable devices. Cataloged as CVE-2023-30799, the shortcoming is expected to put approximately 500,000 and 900,000 RouterOS systems at risk of exploitation via their web and/or Winbox interfaces, respectively, VulnCheck disclosed in a Tuesday report.

A critical severity 'Super Admin' privilege elevation flaw puts over 900,000 MikroTik RouterOS routers at risk, potentially enabling attackers to take full control over a device and remain undetected. The Mikrotik CVE-2023-30799 vulnerability was first disclosed without an identifier in June 2022, and MikroTik fixed the issue in October 2022 for RouterOS stable and on July 19, 2023, for RouterOS Long-term.

"The C2 server serves as a botnet-as-a-service controlling nearly 230,000 vulnerable MikroTik routers," Avast's senior malware researcher, Martin Hron, said in a write-up, potentially linking it to what's now called the M?ris botnet. The botnet is known to exploit a known vulnerability in the Winbox component of MikroTik routers, enabling the attackers to gain unauthenticated, remote administrative access to any affected device.
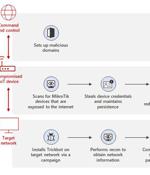
Microsoft on Wednesday detailed a previously undiscovered technique put to use by the TrickBot malware that involves using compromised Internet of Things devices as a go-between for establishing communications with the command-and-control servers. "By using MikroTik routers as proxy servers for its C2 servers and redirecting the traffic through non-standard ports, TrickBot adds another persistence layer that helps malicious IPs evade detection by standard security systems," Microsoft's Defender for IoT Research Team and Threat Intelligence Center said.