Security News

Google has announced new, real-time scanning features for Google Play Protect that make it harder for malicious apps employing polymorphism to evade detection. The problem is that authors of malicious apps promoted outside Google Play have resorted to AI and polymorphic malware that frequently alters identifiable information in a malicious program to bypass automated security platforms, making those scans ineffective.

An updated version of the MATA backdoor framework was spotted in attacks between August 2022 and May 2023, targeting oil and gas firms and the defense industry in Eastern Europe. The updated MATA framework combines a loader, a main trojan, and an infostealer to backdoor and gain persistence in targeted networks.

In contrast, South American organizations experience attack rates of merely 2% largely due to their practice of verifying IDs against government databases, creating a more formidable barrier against fraud. The data analysis underscores a significant and notable discrepancy in attack modes based on document verification compared to attacks using selfies.

A new report from Netskope detailing the top techniques used by cybercriminals to attack organizations found that cloud apps are increasingly being used by threat actors, representing 19% of all clicks on spearphishing links. Netskope recently reported that Microsoft OneDrive is the most popular cloud app used in enterprises, so it is not a surprise that attackers leverage this target a lot, alongside Microsoft Teams, SharePoint and Outlook.

The Android 'SpyNote' malware was observed in attacks targeting Italy using a fake 'IT-alert' public alert service that infected visitors with the information-stealing malware. The APK file installs SpyNote malware on the device, granting it permission to use Accessibility services, which enable the attackers to perform a wide range of dangerous and invasive actions on the compromised device.

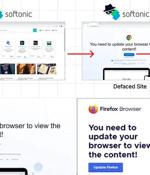
ClearFake, a recently documented threat leveraging compromised WordPress sites to push malicious fake browser updates, is likely operated by the threat group behind the SocGholish "Malware delivery via fake browser updates" campaigns, Sekoia researchers have concluded. Subsequently downloaded payloads create an iframe element to host the fake update interface, download that interface, and the fake update content and HTML page.

Discord continues to be a breeding ground for malicious activity by hackers and now APT groups, with it commonly used to distribute malware, exfiltrate data, and targeted by threat actors to steal authentication tokens. Threat actors abuse Discord in three ways: leveraging its content delivery network to distribute malware, modifying the Discord client to steal passwords, and abusing Discord webhooks to steal data from the victim's system.

A threat actor is using compromised Skype accounts to deliver the DarkGate malware to target organizations, Trend Micro researchers have warned. "Versions of DarkGate have been advertised on Russian language forum eCrime since May 2023. Since then, an increase in the number of initial entry attacks using the malware has been observed," they noted.
Threat actors have been observed serving malicious code by utilizing Binance's Smart Chain (BSC) contracts in what has been described as the "next level of bulletproof hosting." The campaign,...

This is to deal with a recent outbreak of malicious updates pushing malware from compromised publisher accounts. Starting in late August and into September 2023, there has been an elevated number of reports about compromised Steamworks accounts and the attackers uploading malicious builds that infect players with malware.