Security News

Windows has fixed a bug that prevented Mark of the Web flags from propagating to files within downloaded ISO files, dealing a massive blow to malware distributors and developers. According to Bill Demirkapi, an engineer in Microsoft MSRC's Vulnerability and Mitigations team, a bug was fixed that prevented the MoTW flag from propagating to files inside an ISO disk image.

Windows has fixed a bug that prevented Mark of the Web flags from propagating to files within downloaded ISO files, dealing a massive blow to malware distributors and developers. The MoTW flag is added to files as an alternate data stream called 'Zone.Identifier,' which includes what URL security zone the file is from, the referrer, and the URL to the file.

A threat group tracked as 'Worok' hides malware within PNG images to infect victims' machines with information-stealing malware without raising alarms. Avast's report is based on additional artifacts the company captured from Worok attacks, confirming ESET's assumptions about the nature of the PNG files and adding new information on the type of malware payloads and the data exfiltration method.

A malware loader deemed in June to be a "Work in progress" is now fully functional and infecting thousands of Windows corporate and home PCs. IceXLoader version 3 was discovered in the summer by Fortinet's FortiGuard Labs, which wrote that the malware's features were incomplete and it appeared to have been ported to the Nim programming language. IceXLoader was originally sold on the dark web for $118 per lifetime license by a group of developers that also sells other commodity malware and claims to have more than 200 clients, FortiGuard wrote.

Deep Instinct released its 2022 Bi-Annual Cyber Threat Report which focuses on the top malware and ransomware trends and tactics from the first half of 2022 and provides key takeaways and predictions for the ever-evolving cybersecurity threat landscape. "2022 has been another record year for cyber criminals and ransomware gangs. It's no secret that these threat actors are constantly upping their game with new and improved tactics designed to evade traditional cyber defenses," said Mark Vaitzman, Threat Lab Team Leader at Deep Instinct.

A new information-stealing malware named 'StrelaStealer' is actively stealing email account credentials from Outlook and Thunderbird, two widely used email clients. StrelaStealer arrives on the victim's system via email attachments, currently ISO files with varying content.
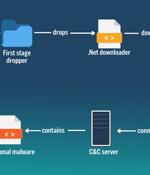
An updated version of a malware loader codenamed IceXLoader is suspected of having compromised thousands of personal and enterprise Windows machines across the world. IceXLoader is a commodity malware that's sold for $118 on underground forums for a lifetime license.

A LockBit 3.0 ransomware affiliate is using phishing emails that install the Amadey Bot to take control of a device and encrypt devices. The Amadey Bot malware is an old strain capable of performing system reconnaissance, data exfiltration, and payload loading.

Cryptocurrency users are being targeted with a new clipper malware strain dubbed Laplas by means of another malware known as SmokeLoader. Observed in the wild since circa 2013, SmokeLoader functions as a generic loader capable of distributing additional payloads onto compromised systems, such as information-stealing malware and other implants.

Roid users are often advised to get mobile apps from Google Play, the company's official app marketplace, to minimize the possibility of downloading malware. "Distribution through droppers on official stores remains one of the most efficient ways for threat actors to reach a wide and unsuspecting audience. Although other distribution methods are also used depending on cybercriminals targets, resources, and motivation, droppers remain one of the best option on price-efforts-quality ratio, competing with SMiShing," Threat Fabric researchers recently pointed out, after sharing their discovery of several apps on Google Play functioning as droppers for the Sharkbot and Vultur banking trojans.