Security News

A new piece of JavaScript malware has been observed attempting to steal users' online banking account credentials as part of a campaign that has targeted more than 40 financial institutions across...

IBM Security has dissected some JavaScript code that was injected into people's online banking pages to steal their login credentials, saying 50,000 user sessions with more than 40 banks worldwide were compromised by the malicious software in 2023. This injected code executes on the page in the browser, and intercepts the victim's credentials as they are entered, which can be passed to fraudsters to exploit to drain accounts.

CEO, fresh with funds, lays out the dependency dilemma Interview Open source security biz Socket is extending its source code dependency checker, which previously addressed only JavaScript and...

The npm Public Registry, a database of JavaScript packages, fails to compare npm package manifest data with the archive of files that data describes, creating an opportunity for the installation and execution of malicious files. "The npm Public Registry does not validate manifest information with the contents of the package tarball, relying instead on npm-compatible clients to interpret and enforce validation/consistency," Clarke explains.

Security researchers discovered a new malicious tool they named PindOS that delivers the Bumblebee and IcedID malware typically associated with ransomware attacks. PindOS is a simple JavaScript malware dropper that appears to be built specifically to fetch the next-stage payloads that deliver the attackers' final payload. Simple JavaScript malware dropper.
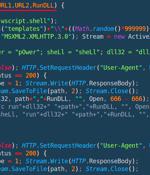
A new strain of JavaScript dropper has been observed delivering next-stage payloads like Bumblebee and IcedID. Cybersecurity firm Deep Instinct is tracking the malware as PindOS, which contains the name in its "User-Agent" string. Both Bumblebee and IcedID serve as loaders, acting as a vector for other malware on compromised hosts, including ransomware.

A fresh round of patches has been made available for the vm2 JavaScript library to address two critical flaws that could be exploited to break out of the sandbox protections. Both the flaws - CVE-2023-29199 and CVE-2023-30547 - are rated 9.8 out of 10 on the CVSS scoring system and have been addressed in versions 3.9.16 and 3.9.17, respectively.

Back in 2022, about a code execution hole in the widely-used JavaScript sandbox system vm2. Your web browser is a good example of a sandbox, which is how it keeps control over JavaScript programs that it downloads and runs from remote websites.

Proof-of-concept exploit code has been released for a recently disclosed critical vulnerability in the popular VM2 library, a JavaScript sandbox that is used by multiple software to run code securely in a virtualized environment. The researchers who found that the VM2 library handled improperly the host objects passed to the 'Error.

They existed simply as placeholders for README files that included the final links that the crooks wanted people to click on. These links typically including referral codes that would net the scammers a modest reward, even if the person clicking through was doing so simply to see what on earth was going on.