Security News

A new security flaw has been disclosed in the Google Cloud Platform's Cloud SQL service that could be potentially exploited to obtain access to confidential data. "The vulnerability could have enabled a malicious actor to escalate from a basic Cloud SQL user to a full-fledged sysadmin on a container, gaining access to internal GCP data like secrets, sensitive files, passwords, in addition to customer data," Israeli cloud security firm Dig said.

As part of Google's commitment to building a strong cybersecurity workforce, the Google Cybersecurity Certificate offers an affordable and accessible pathway to a career in cybersecurity. Despite the urgent need to address this threat, there are currently more than 750,000 unfilled cybersecurity jobs in the U.S. We launched the new Cybersecurity Certificate to help employers fill critical roles, and to level the playing field for people of all backgrounds to enter the cybersecurity workforce.

Google's cloud division is following in the footsteps of Microsoft with the launch of Security AI Workbench that leverages generative AI models to gain better visibility into the threat landscape.Users, like with Microsoft's GPT-4-based Security Copilot, can "Conversationally search, analyze, and investigate security data" with an aim to reduce mean time-to-respond as well as quickly determine the full scope of events.

Cybersecurity researchers have disclosed details of a now-patched zero-day flaw in Google Cloud Platform that could have enabled threat actors to conceal an unremovable, malicious application inside a victim's Google account. "The vulnerability allows attackers to gain permanent and unremovable access to a victim's Google account by converting an already authorized third-party application into a malicious trojan app, leaving the victim's personal data exposed forever," Astrix said in a report.

Open source software and software supply chain security risks continue to be a primary concern for developers and organizations. According to a 2022 study by electronic design and automation company Synopsys, 84% of open source software codebases contained at least one known vulnerability - a nearly 4% increase from last year - and 48% contained a high-risk vulnerability.

Malicious actors can take advantage of "Insufficient" forensic visibility into Google Cloud Platform to exfiltrate sensitive data, a new research has found. "Unfortunately, GCP does not provide the level of visibility in its storage logs that is needed to allow any effective forensic investigation, making organizations blind to potential data exfiltration attacks," cloud incident response firm Mitiga said in a report.

Attackers can exfiltrate company data stored in Google Cloud Platform storage buckets without leaving obvious forensic traces of the malicious activity in GCP's storage access logs, Mitiga researchers have discovered. "In normal usage, files inside storage objects are read multiple times a day as part of day-to-day activity of the organization," Mitiga cloud incident responder Veronica Marinov noted.

Google closed its $5.4 billion Mandiant acquisition today in a move that brings the threat intel and incident response giant under the Google Cloud umbrella. Six months and one shareholder lawsuit later, the two companies' combined services and products help customers shift to a "More proactive approach" to security operations, according to Google Cloud CEO Thomas Kurian.
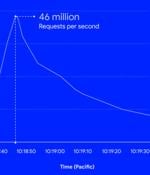
Google's cloud division on Thursday disclosed it mitigated a series of HTTPS distributed denial-of-service attacks which peaked at 46 million requests per second, making it the largest such recorded to date. The attack, which occurred on June 1, targeting an unnamed Google Cloud Armor customer, is 76% larger than the 26 million RPS DDoS attack repealed by Cloudflare earlier this June.

Microsoft announced today that Microsoft Defender for Cloud now also comes with native protection for Google Cloud Platform environments, providing security recommendations and threat detection across clouds. Defender for Cloud is a security solution that monitors cloud services for threats, makes recommendations to harden security posture, and detects and warns of vulnerabilities in protected multi-cloud and hybrid environments.