Security News

Google Cloud has addressed a medium-severity security flaw in its platform that could be abused by an attacker who already has access to a Kubernetes cluster to escalate their privileges. "An...

Generative AI can be used by attackers, but security professionals shouldn't lose sleep over it, according to a Google Cloud threat intelligence analyst. Google Cloud's team recently spoke about the most notable cybersecurity threats of 2023 - multi-faceted extortion and zero-day exploitation - and predicted more zero-day attacks in 2024, during two public, virtual sessions.

What will cybersecurity look like in 2024? Google Cloud's global Cybersecurity Forecast found that generative AI can help attackers and defenders and urged security personnel to look out for nation-state backed attacks and more. Threat actors will use generative AI and large language models in phishing and other social engineering scams, Google Cloud predicted.

Google is asking bug hunters and exploit writers to develop 0-day and n-day exploits in Chrome's V8 JavaScript engine and Google Cloud's Kernel-based Virtual Machine. The exploit writers should make their exploitation attempts against a V8 version running on Google infrastructure.

Infosec in brief A security weakness in Google Cloud Build could have allowed attackers to tamper with organizations' code repositories and application images, according to Orca Security researchers. The issue, as Google describes it, is more about poorly defined permissions.
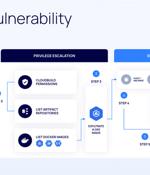
Cybersecurity researchers have uncovered a privilege escalation vulnerability in Google Cloud that could enable malicious actors tamper with application images and infect users, leading to supply chain attacks. The issue, dubbed Bad.Build, is rooted in the Google Cloud Build service, according to cloud security firm Orca, which discovered and reported the issue.

A critical design flaw in the Google Cloud Build service discovered by cloud security firm Orca Security can let attackers escalate privileges, providing them with almost nearly-full and unauthorized access to Google Artifact Registry code repositories. Dubbed Bad.Build, this flaw could enable the threat actors to impersonate the service account for the Google Cloud Build managed continuous integration and delivery service to run API calls against the artifact registry and take control over application images.

A criminal crew with a history of deploying malware to harvest credentials from Amazon Web Services accounts may expand its attention to organizations using Microsoft Azure and Google Cloud Platform. The crooks used to target primarily AWS users, and now seem to be looking for ways into Azure and Google Cloud accounts.
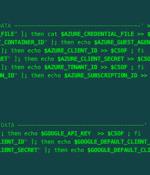
A malicious actor has been linked to a cloud credential stealing campaign in June 2023 that's focused on Azure and Google Cloud Platform services, marking the adversary's expansion in targeting beyond Amazon Web Services. They also overlap with an ongoing TeamTNT campaign disclosed by Aqua called Silentbob that leverages misconfigured cloud services to drop malware as part of what's said to be a testing effort, while also linking SCARLETEEL attacks to the threat actor, citing infrastructure commonalities.

Google Cloud's AML AI represents an advancement in the fight against money laundering. In this Help Net Security interview, Anna Knizhnik, Director, Product Management, Cloud AI, Financial Services, at Google Cloud, explains how Google Cloud's AML AI outperforms current systems, lowers operational costs, enhances governance, and improves the customer experience by reducing false positives and minimizing compliance verification checks.