Security News

At this week's event, Google presented its latest solutions as it tries to overtake Amazon and Microsoft in the cloud market. The post Google Next ’22: A new era of built-in cloud services...
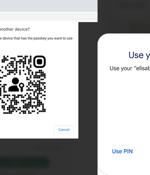
Google on Wednesday officially rolled out support for passkeys, the next-generation authentication standard, to both Android and Chrome. "Passkeys are a significantly safer replacement for passwords and other phishable authentication factors," the tech giant said.

Google announced today that it's introducing passkey support to its Chrome web browser and the Android operating system to simplify sign-ins across apps, websites, and devices. "Passkeys are a significantly safer replacement for passwords and other phishable authentication factors. They cannot be reused, don't leak in server breaches, and protect users from phishing attacks," Google said today.

In the latest attacks, phishing emails impersonate the U.S. Small Business Administration and abuse Google Forms to host phishing pages that steal the personal details of business owners. The lures used in the phishing emails are for pandemic financial support programs like the "Paycheck Protection Program", "Revitalization Fund", and "COVID Economic Injury Disaster Loan.".

Mandia spoke with reporters for the first time about his threat-intel-slash-incident-response company's new owner during a press briefing ahead of Google Cloud Next, which kicked off today in San Francisco and virtually. Google Cloud brings expertise in big data, analytics, and artificial intelligence, he added.

Google has announced more details regarding turning off support for the Google Chrome Manifest V2 extension as the company pushes more developers to transition to Manifest V3. An update from the Chrome team says that they will proceed in careful, experimental steps, ensuring a smooth end-user experience during the phase-out of Manifest V2 in June 2023. In January 2022, the Chrome Web Store stopped accepting new extensions built on Manifest V2. According to the original roll-out timeline released by Google a year ago, starting from January 2023, all extensions built on Manifest V2 would stop working on the Chrome browser.

Security researchers have discovered 75 applications on Google Play and another ten on Apple's App Store engaged in ad fraud. The Satori team have informed Google and Apple about their findings and the apps have been removed from the official Android and iOS stores.

Wearable technology company Fitbit has announced a new clause that requires users to switch to a Google account "Sometime" in 2023. "In 2023, we plan to launch Google accounts on Fitbit, which will enable use of Fitbit with a Google account," the Google-owned fitness devices maker said.

Malwarebytes has addressed an issue that prevented users from accessing websites and services hosted on the google.com domain, including Google search and Youtube. According to a large number of reports from people affected by this, their browsers were prevented from accessing Google sites after Malwarebytes flagged and blocked them as malicious.

Google and its Youtube domains are being flagged as malicious by Malwarebytes as of Wednesday morning, blocking users from accessing a whole range of websites. "Malwarebytes is aware of a temporary issue with the web filtering component of our product that may be blocking certain domains, including google.com," a Malwarebytes spokesperson told The Register.