Security News

The particular provision requires web browsers like Chrome, Safari, and Firefox to accept QWACs, which practically compels browser developers and security advocates to ease their security stance. TLS certificates are vital for the online exchange of sensitive information with websites such as passwords, sensitive uploads, or payment details.

Let's Encrypt, a non-profit organization that helps people obtain free SSL/TLS certificates for websites, plans to revoke a non-trivial number of its certs on Friday because they were improperly issued. In a post to the Let's Encrypt discussion community forum, site reliability engineer Jillian Tessa explained that on Tuesday, a third party reported "Two irregularities" in the code implementing the "TLS Using ALPN" validation method in Boulder, its Automatic Certificate Management Environment software.

Let's Encrypt will begin revoking certain SSL/TLS certificates issued within the last 90 days starting January 28, 2022. As a non-profit certificate authority run by Internet Security Research Group, Let's Encrypt provides X.509 certificates for Transport Layer Security encryption at no cost.

Another CISO walks into a board meeting and muddles through stats showing their compliance status. In the classic risk management equation of Risk = Threat x Vulnerability, I have no control over the threat actor's motivation, skill, or resources.

The challenge faced by already strained IT teams is how to deliver strong certificate management across increasingly complex IT environments, at a time when workforces are massively distributed and entering the corporate network via the consumer-grade technologies in their homes. While third-party certificate authorities are a trusted option for many enterprises across the globe, many choose instead to issue them in-house, operating their own "Private CAs" to fulfill at least a portion of their PKI needs.
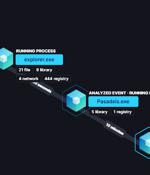
Cybersecurity researchers have disclosed details of an evasive malware campaign that makes use of valid code signing certificates to sneak past security defenses and stay under the radar with the goal of deploying Cobalt Strike and BitRAT payloads on compromised systems. The binary, a loader, has been dubbed "Blister" by researchers from Elastic Security, with the malware samples having negligible to zero detections on VirusTotal.

Driven by the acceleration of digital transformation and cloud migration during the pandemic, the analysis of the world's top 1 million sites over the last 18 months shows that in many ways, the internet is becoming more secure. Despite the adoption of stronger encryption protocols, many companies continue to use legacy RSA encryption algorithms to generate keys, which in conjunction with TLS certificates, act as machine identities that authorize secure connections between physical, virtual and IoT devices, APIs, applications and clusters.

Security researchers have checked the web's public key infrastructure and have measured a long-known but little-analyzed security threat: hidden root Certificate Authorities. You can be reasonably confident that your bank website is actually your bank website when it presents your browser with an end-user or leaf certificate that's linked through a chain of trust to an intermediate certificate and ultimately the X.509 root certificate of a trusted CA. Each browser relies on a trust store consisting of a hundred or so root certificates that belong to a smaller set of organizations.

Microsoft has released the KB5008295 out-of-band update to address Windows 11 issues while opening or using some built-in apps and features due to an expired Microsoft digital certificate. "Devices directly connected to Windows Update and Windows Update for Business should be offered and automatically install KB5008295 to resolve the issues," Microsoft explained.

Apple fixes security feature bypass in macOSApple has delivered a barrage of security updates for most of its devices this week, and among the vulnerabilities fixed are CVE-2021-30892, a System Integrity Protection bypass in macOS, and CVE-2021-30883, an iOS flaw that's actively exploited by attackers. Good security habits: Leveraging the science behind how humans develop habitsIn this interview with Help Net Security, George Finney, CSO at Southern Methodist University, explains what good security habits are, how to successfully implement them and why are they important.