Security News
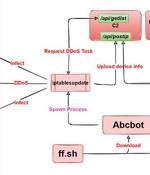
Researchers from Qihoo 360's Netlab security team have released details of a new evolving botnet called "Abcbot" that has been observed in the wild with worm-like propagation features to infect Linux systems and launch distributed denial-of-service attacks against targets. While the earliest version of the botnet dates back to July 2021, new variants observed as recently as October 30 have been equipped with additional updates to strike Linux web servers with weak passwords and are susceptible to N-day vulnerabilities, including a custom implementation of DDoS functionality, indicating that the malware is under continuous development.

The new BotenaGo malware botnet has been discovered using over thirty exploits to attack millions of routers and IoT devices. CVE-2020-8958: Guangzhou 1GE ONU. Researchers at AT&T who analyzed the new botnet found that it targets millions of devices with functions that exploit the above flaws.

The U.S. Department of Justice sentenced a Russian man for operating a large-scale digital advertising fraud scheme called 'Methbot' that stole at least $7 million from American companies. Aleksandr Zhukov, aka the "King of Fraud," was sentenced to 10 years of imprisonment in the U.S. and ordered to forfeit the total sum of his assets, amounting to $3,827,493.

The Global Threat Landscape Report indicates a drastic rise in sophisticated cyberattacks targeting digital infrastructures, organizations, and individuals in 2021. Organizations struggle to address these threats due to their resource sophistication and their lack of understanding of evolving threat landscapes.

Cybersecurity researchers disclosed details of what they say is the "Largest botnet" observed in the wild in the last six years, infecting over 1.6 million devices primarily located in China, with the goal of launching distributed denial-of-service attacks and inserting advertisements into HTTP websites visited by unsuspecting users. Mainly targeting MIPS-based fiber routers, the botnet leverages a combination of third-party services such as GitHub, peer-to-peer networks, and central command-and-control servers for its bots to controller communications, not to mention completely encrypting the transmission channels to prevent the victimized devices from being taken over.

The PurpleFox botnet has refreshed its arsenal with new vulnerability exploits and dropped payloads, now also leveraging WebSockets for C2 bidirectional communication. Although it's mainly based in China, the PurpleFox botnet still has a global presence through hundreds of compromised servers.

The PurpleFox botnet has refreshed its arsenal with new vulnerability exploits and dropped payloads, now also leveraging WebSockets for C2 bidirectional communication. Although it's mainly based in China, the PurpleFox botnet still has a global presence through hundreds of compromised servers.

Threat group FreakOut's Necro botnet has developed a new trick: infecting Visual Tools DVRs with a Monero miner. Juniper Threat Labs researchers have issued a report detailing new activities from FreakOut, also known as Necro Python and Python.

The MyKings botnet is still actively spreading, making massive amounts of money in crypto, five years after it first appeared in the wild. Being one of the most analyzed botnets in recent history, MyKings is particularly interesting to researchers thanks to its vast infrastructure and versatile features, including bootkits, miners, droppers, clipboard stealers, and more.

A new update to the FreakOut Python botnet has added a recently published PoC exploit for Visual Tools DVR in its arsenal to further aid in breaching systems. Mining Monero on a DVR. Researchers at Juniper Threat Labs have analyzed a recent sample of the malware, and warn that Visual Tools DVR VX16 4.2.28.0 from visual-tools.com is being targeted with an exploit for a CVE-less flaw.