Security News

Several malicious Google Play Android apps installed over 2 million times push intrusive ads to users while concealing their presence on the infected devices. Dr. Web explains that once victims install these apps on their devices, they hide by replacing their icons with that of Google Chrome or using a transparent icon image to create empty space in the app drawer.

A custom Flipper Zero firmware called 'Xtreme' has added a new feature to perform Bluetooth spam attacks on Android and Windows devices. The main idea behind the spam attack is to use Flipper Zero's wireless communication capabilities to spoof advertising packets and transmit them to devices in range of pairing and connection requests.
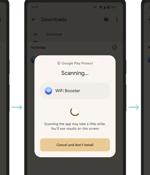
Google has announced an update to its Play Protect with support for real-time scanning at the code level to tackle novel malicious apps prior to downloading and installing them on Android devices....

Google has announced new, real-time scanning features for Google Play Protect that make it harder for malicious apps employing polymorphism to evade detection. The problem is that authors of malicious apps promoted outside Google Play have resorted to AI and polymorphic malware that frequently alters identifiable information in a malicious program to bypass automated security platforms, making those scans ineffective.

The Android 'SpyNote' malware was observed in attacks targeting Italy using a fake 'IT-alert' public alert service that infected visitors with the information-stealing malware. The APK file installs SpyNote malware on the device, granting it permission to use Accessibility services, which enable the attackers to perform a wide range of dangerous and invasive actions on the compromised device.

Israeli Android users are targeted by a malicious version of the 'RedAlert - Rocket Alerts' app that, while it offers the promised functionality, acts as spyware in the background. RedAlert - Rocket Alerts is a legitimate open-source app used by Israeli citizens to receive notifications of incoming rockets targeting the country.
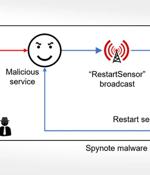
The Android banking trojan known as SpyNote has been dissected to reveal its diverse information-gathering features. Typically spread via SMS phishing campaigns, attack chains involving the...

An ad fraud botnet dubbed PEACHPIT leveraged an army of hundreds of thousands of Android and iOS devices to generate illicit profits for the threat actors behind the scheme. The botnet is part of...

Singapore-based infosec outfit Group-IB on Thursday released details of a new Android trojan that exploits the operating system's accessibility features to steal info that enables theft of personal information. The security research outfit wrote that the trojan, named GoldDigger, currently targets Vietnamese banking apps - but includes code suggesting its developers plan wider attacks.
A new Android banking trojan named GoldDigger has been found targeting several financial applications with an aim to siphon victims' funds and backdoor infected devices. "The malware targets more...