Security News

After releasing the Open Source Vulnerabilities database in February, Google has launched the OSV-Scanner, a free command line vulnerability scanner that open source developers can use to check for vulnerabilities in their projects' dependencies. Finding vulnerabilities in open-source dependencies.

Unknown threat actors have uploaded a massive 144,294 phishing-related packages on open-source package repositories, inluding NPM, PyPi, and NuGet. The large-scale attack resulted from automation, as the packages were uploaded from accounts using a particular naming scheme, featured similar descriptions, and led to the same cluster of 90 domains that hosted over 65,000 phishing pages.

Google on Tuesday announced the open source availability of OSV-Scanner, a scanner that aims to offer easy access to vulnerability information about various projects. The Go-based tool, powered by the Open Source Vulnerabilities database, is designed to connect "a project's list of dependencies with the vulnerabilities that affect them," Google software engineer Rex Pan in a post shared with The Hacker News.

New research from Endor Labs offers a view into the rampant but often unmonitored use of existing open-source software in application development and the dangers arising from this common practice. As just one example, the research reveals that 95% of all vulnerabilities are found in transitive dependencies - open-source code packages that developers do not select, but are indirectly pulled into projects.

ConductorOne open-sourced their identity connectors in a project called Baton, available on GitHub. Each connector gives developers the ability to extract, normalize, and interact with workforce...
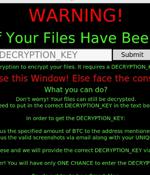
A version of an open source ransomware toolkit called Cryptonite has been observed in the wild with wiper capabilities due to its "Weak architecture and programming." Written in Python, the malware employs the Fernet module of the cryptography package to encrypt files with a ".

Open source software hosting and cloud computing provider Fosshost will no longer be providing services as it reaches end of life. UK-based non-profit Fosshost has been providing services to several high profile open source projects like GNOME, Armbian, Debian and Free Software Foundation Europe completely free of charge.
CI Fuzz CLI, the open-source Command-Line Interface tool from Code Intelligence, now allows Java developers to easily incorporate fuzz testing into their existing JUnit setup to find functional bugs and security vulnerabilities at scale. CI Fuzz CLI, available on GitHub, leverages genetic and evolutionary algorithms and automated instrumentation to dynamically generate millions of unusual inputs to test Java applications for unexpected behaviors that may lead to crashes, DoS or zero-day exploits.

Open source tools are a key part of the Kubernetes security environment, with most companies using open source Kubernetes security software, research by ARMO has revealed. In a survey of The State of Kubernetes Open Source Security, 55% of respondents said they used at least some open source tools to keep their Kubernetes clusters safe; this includes those who use purely open source and those mix open source and proprietary solutions.

Provectus released v0.8 of its Open Data Discovery Platform, an open-source platform that helps data-driven enterprises democratize their data. Designed to overcome the limitations of conventional data catalogs, ODD helps to standardize data collection, improves compatibility of different catalogs, expands data lineage capabilities, and enhances data quality and observability.